Innovative use of recycled textile fibers in building materials: A circular economy approach
(1) Raha International School, (2) Dental Clinic Abu Dhabi
https://doi.org/10.59720/25-218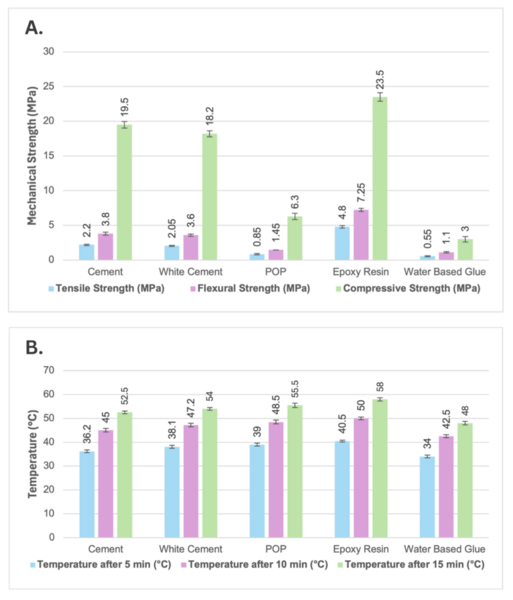
The fast fashion industry is responsible for producing millions of tons of textile waste annually, contributing significantly to environmental degradation through landfill accumulation and carbon emissions. Addressing this growing challenge, the present research explores an innovative approach to repurposing textile waste by converting it into sustainable building materials. This study examines whether recycled textile fibers can enhance the mechanical and thermal performance of composite bricks with different binders, testing the hypothesis that those reinforced with epoxy resin and cement exhibit the highest mechanical strength (compressive, tensile, and flexural), while those using water-based glue and plaster of Paris (POP) demonstrate superior thermal insulation due to their porous structure. To test this hypothesis, we manually processed textile waste into fine fibers, mixed the fibers with selected binders, and molded and air-dried the mixtures into composite bricks. We then evaluated their performance by applying mechanical loads to assess compressive, tensile, and flexural strength, and by measuring heat transfer across the bricks under controlled heating conditions. Epoxy- and cement-based composites offered greater mechanical durability, while glue- and POP-based bricks provided better insulation performance. These differences suggest potential for application-specific use: epoxy and cement composites for structural or semi-structural roles and glue or POP composites for interior insulation and decorative purposes. Beyond performance, the study underscores the environmental benefits of textile reuse. Converting discarded fabrics into building materials diverts waste from landfills, supports energy efficiency, and reduces the carbon footprint of conventional construction. The findings highlight the potential of circular economy principles to drive sustainable development and guide future research in optimizing performance and scalability.
This article has been tagged with: