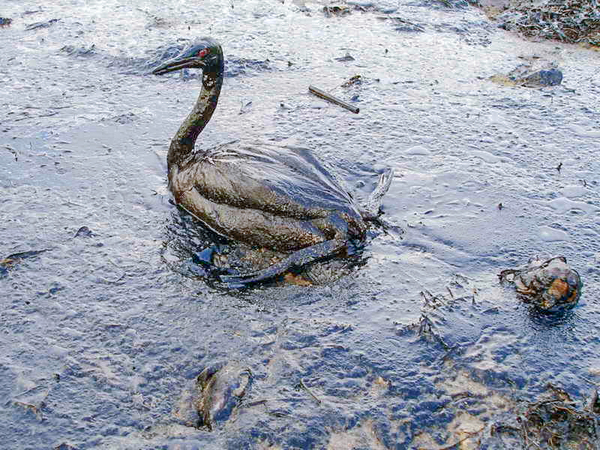
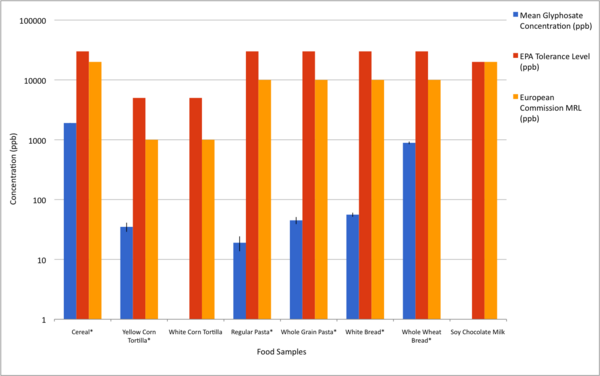
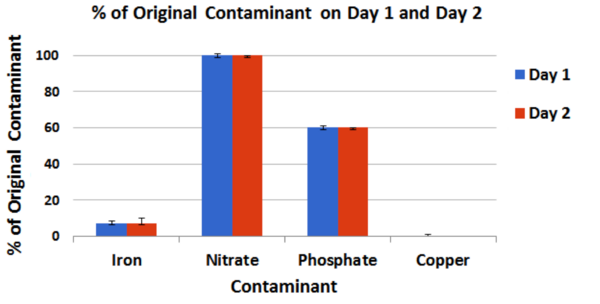
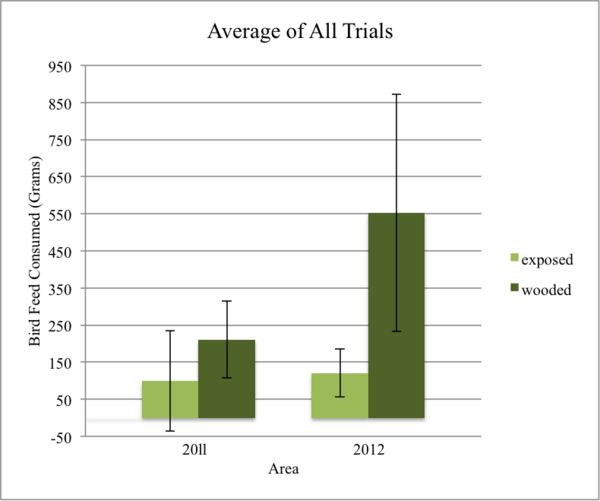
Engineered bacteria that degrade oil are currently being considered as a safe option for the treatment of oil spills. For this approach to be successful, the bacteria must effectively express oil-degrading genes they uptake as part of an external genoming vehicle called a "plasmid". Using a computational approach, the authors investigate plasmid-bacterium compatibility to find pairs that ensure high levels of gene expression.
Read More...