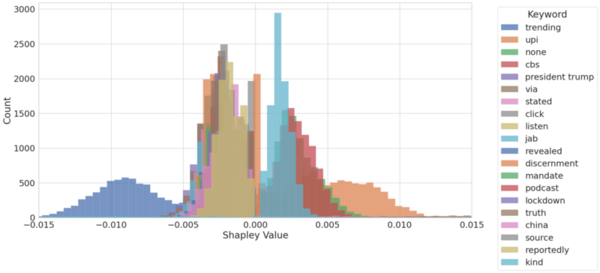
Here, the authors sought to develop a new metric to evaluate the efficacy of baseball pitchers using machine learning models. They found that the frequency of balls, was the most predictive feature for their walks/hits allowed per inning (WHIP) metric. While their machine learning models did not identify a defining trait, such as high velocity, spin rate, or types of pitches, they found that consistently pitching within the strike zone resulted in significantly lower WHIPs.
Read More...