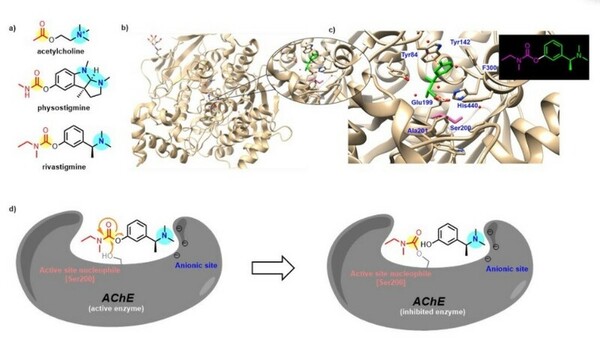
Naturally occurring neuroactive alkaloids are often studied for their potential to treat Neurological diseases. This team of students study Rivastigmine, a potent cholinesterase inhibitor that is a synthetic analog of physostigmine, which comes from the Calabar bean plant Physostigma venenosum. By comparing the effects of optimized synthetic analogs to the naturally occurring alkaloid, they determine the most favorable analog for inhibition of acetylcholinesterase (AChE), the enzyme that breaks down the neurotransmitter acetylcholine (ACh) to terminate neuronal transmission and signaling between synapses.
Read More...