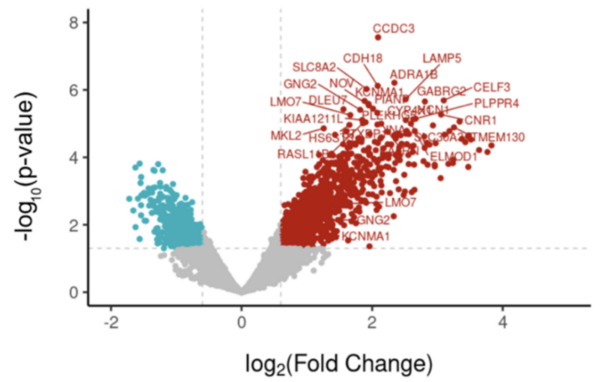
The authors looked at genes that were differentially expressed in patients who had and had not had febrile seizures to determine what differences in gene expression existed.
Read More...Gene expression analysis of febrile seizure’s impact on mesial temporal lobe epilepsy

The authors looked at genes that were differentially expressed in patients who had and had not had febrile seizures to determine what differences in gene expression existed.
Read More...Gene expression profiling of MERS-CoV-London strain
%20(1).png)
In this study, the authors identify transcripts and gene networks that are changed after infection with the Middle East Respiratory Syndrome-related coronavirus (MERS-CoV).
Read More...Transcriptomic profiling identifies differential gene expression associated with childhood abuse
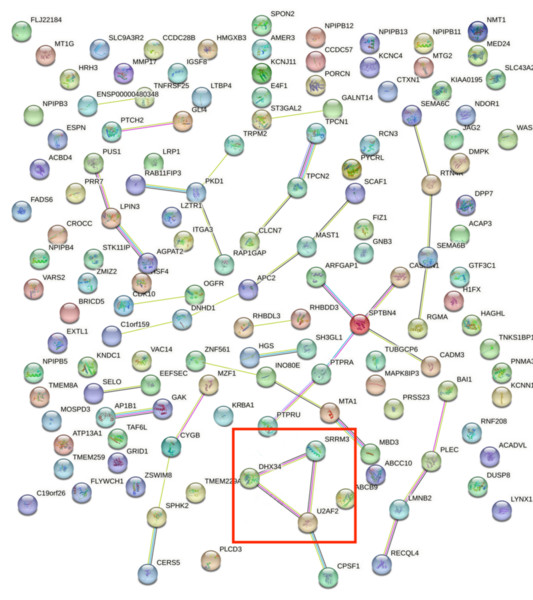
Childhood abuse has severe and lasting effects throughout an individual's life, and may even have long-term biological effects on individuals who suffer it. To learn more about the effects of abuse in childhood, Li and Yearwood analyze gene expression data to look for genes differentially expressed genes in individuals with a history of childhood abuse.
Read More...Analysis of complement system gene expression and outcome across the subtypes of glioma
Here the authors sought to better understand glioma, cancer that occurs in the glial cells of the brain with gene expression profile analysis. They considered the expression of complement system genes across the transcriptional and IDH-mutational subtypes of low-grade glioma and glioblastoma. Based on their results of their differential gene expression analysis, they found that outcomes vary across different glioma subtypes, with evidence suggesting that categorization of the transcriptional subtypes could help inform treatment by providing an expectation for treatment responses.
Read More...Characterization of Inflammatory Cytokine Gene Expression in a Family with a History of Psoriasis
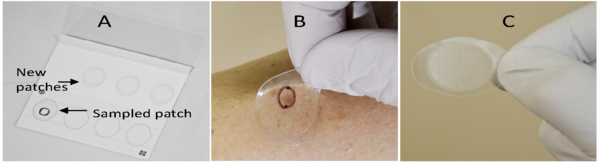
Psoriasis is a heritable autoimmune disorder characterized by abnormal red and itchy skin patches. The authors study the family of a man with psoriasis. They explore whether the man's children, who do not show any symptoms of psoriasis, demonstrate gene expression consistent with the disease.
Read More...Investigating KNOX Gene Expression in Aquilegia Petal Spur Development
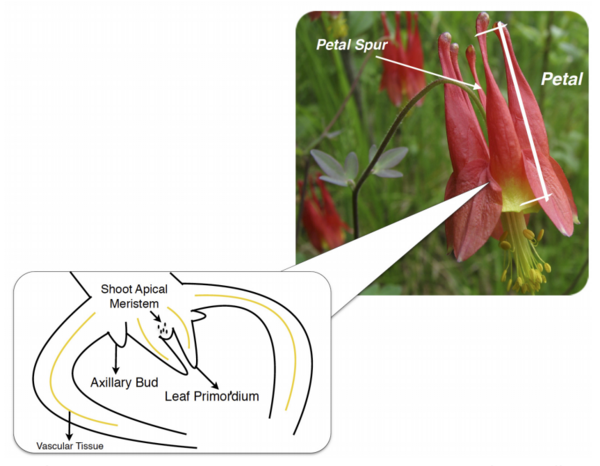
Plants, and all other multi-cellular organisms, develop through the coordinated action of many sets of genes. The authors here investigate the genes, in a class named KNOX, potentially responsible for organizing a certain part of Aquilegia (columbine) flowers called petal spurs. Through the technique Reverse Transcription-Polymerase Chain Reaction (RT-PCR), they find that certain KNOX genes are expressed non-uniformly in petal spurs, suggesting that they may be involved, perhaps in a cell-specific manner. This research will help guide future efforts toward understanding how many beautiful flowers develop their unique shapes.
Read More...Impact of TCERG1 SNP on gene expression and protein interactome in Huntington’s disease
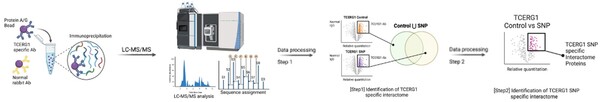
The authors assess a genetic variant within a well-known interaction partner of huntingtin that has been linked to modifying the age of onset of Huntington's disease.
Read More...Identification of potential therapeutic targets for multiple myeloma by gene expression analysis
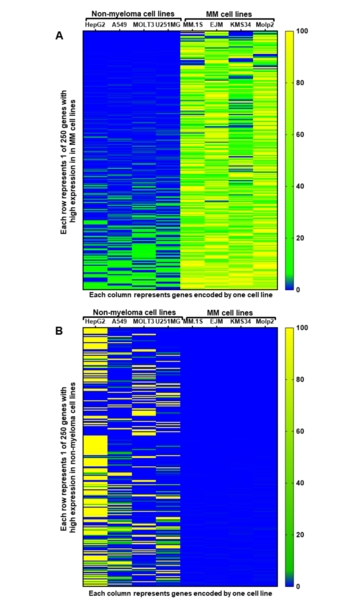
A central challenge of cancer therapy is identifying treatments that will effectively target cancer cells while minimizing effects on healthy cells. To identify potential targets for treating a multiple myeloma, a frequently incurable cancer, Kochenderfer and Kochenderfer analyze RNA sequencing data from the Cancer Cell Line Encyclopedia to find genes with high expression in multiple myeloma cells and low expression in normal tissues
Read More...Investigating the effects of mutations of amino acids on the protein expression of CDK2 cancer gene
Expressional correlations between SERPINA6 and pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma-linked genes
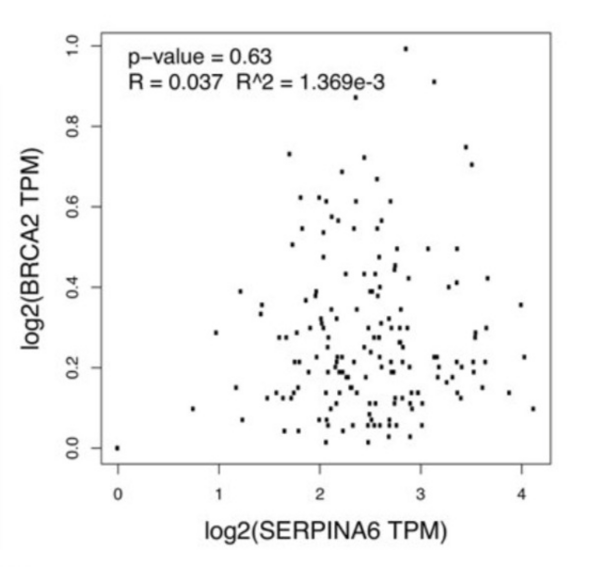
Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) is the most common form of pancreatic cancer, with early diagnosis and treatment challenges. When any of the genes KRAS, SMAD4, TP53, and BRCA2 are heavily mutated, they correlate with PDAC progression. Cellular stress, partly regulated by the gene SERPINA6, also correlates with PDAC progression. When SERPINA6 is highly expressed, corticosteroid-binding globulin inhibits the effect of the stress hormone cortisol. In this study, the authors explored whether there is an inverse correlation between the expression of SERPINA6 and PDAC-linked genes.
Read More...