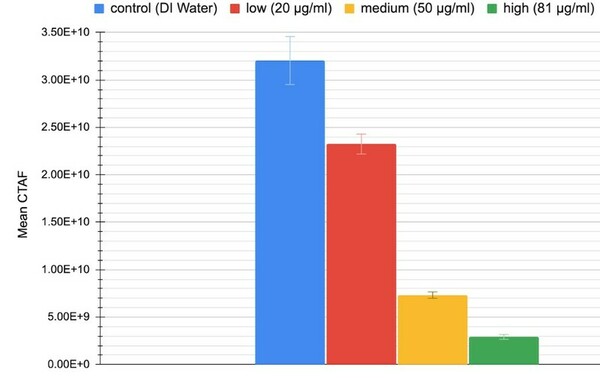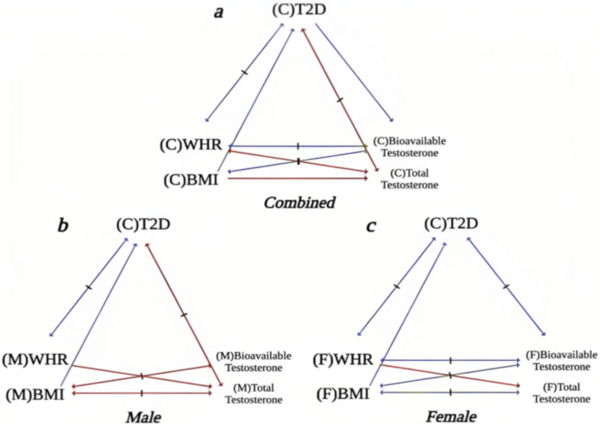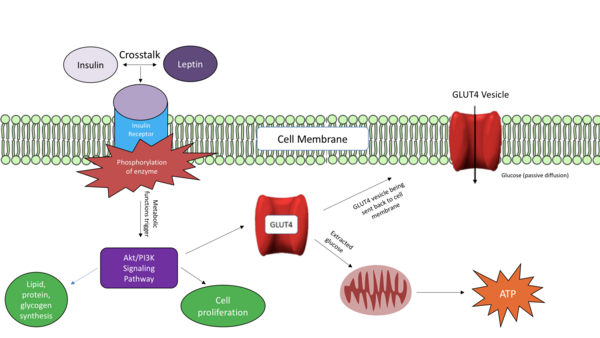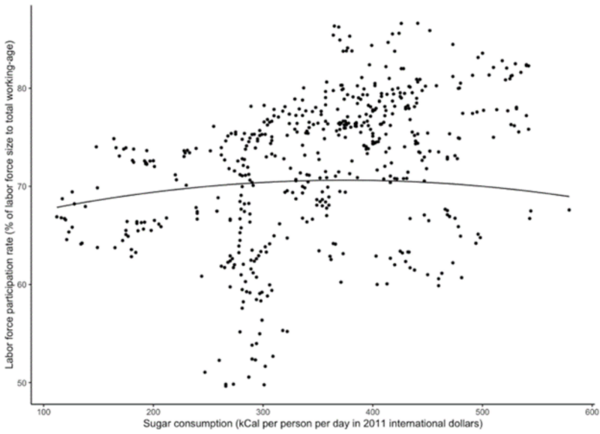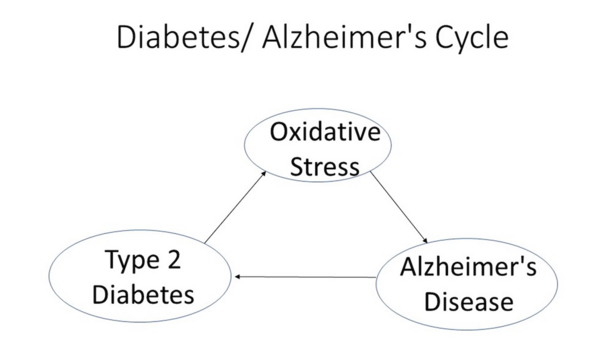
Studies show an age-related link between Alzheimer’s Disease and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus with oxidative stress a characteristic of both. Here, methanolic fractionations and extracts of four Ayurvedic plants were assessed for their protective abilities using a number of in vitro assays. Extracts inhibited oxidative stress and reduced activity of key enzymes involved in the pathogenesis of both diseases in neuroblastoma cells.
Read More...