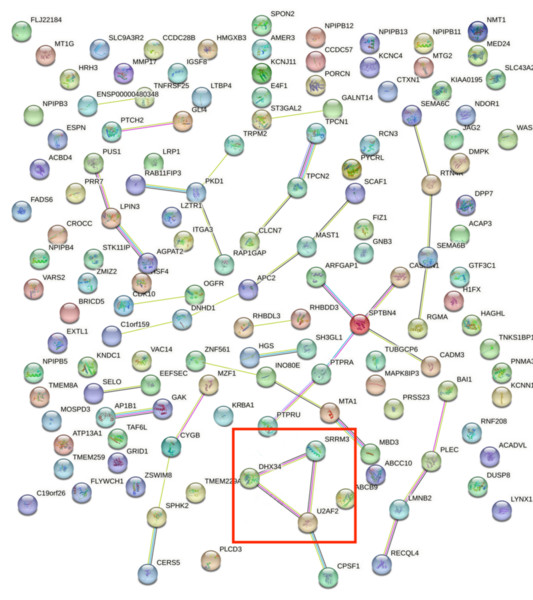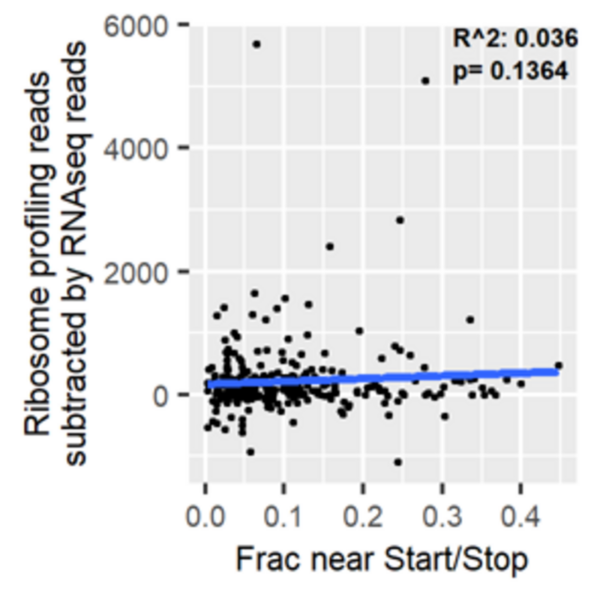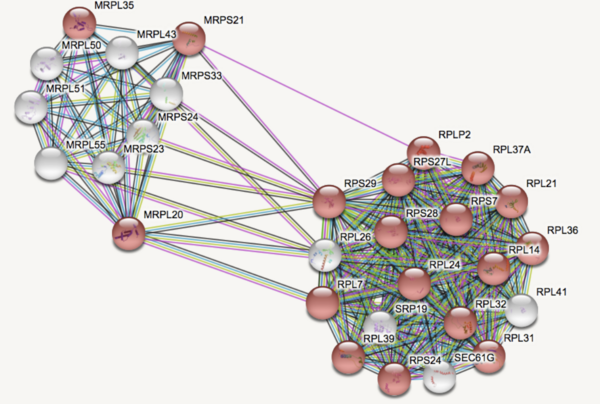
Major Depressive Disorder (MDD), and Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD) are two of the fastest growing comorbid diseases in the world. Using publicly available datasets from the National Institute for Biotechnology Information (NCBI), Ravi and Lee conducted a differential gene expression analysis using 184 blood samples from either control individuals or individuals with comorbid MDD and PTSD. As a result, the authors identified 253 highly differentially-expressed genes, with enrichment for proteins in the gene ontology group 'Ribosomal Pathway'. These genes may be used as blood-based biomarkers for susceptibility to MDD or PTSD, and to tailor treatments within a personalized medicine regime.
Read More...