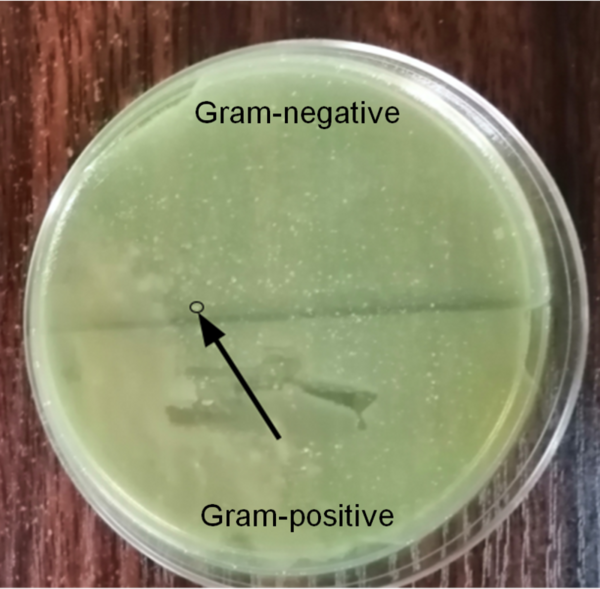
Antibiotics are one of the most common treatments for bacterial infections, but the emergence of antibiotic resistance is a major threat to the control of infectious diseases. Many factors contribute to the development of antibiotic resistance. One is bacterial conjugation from Gram-positive to Gram-negative bacteria where there is a transfer of resistance genes from Gram-positive to Gram-negative bacteria that could increase antibiotic resistance in the latter. In light of these observations, we decided to test whether Gram-negative bacteria that came into contact with Gram-positive bacteria had a higher resistance to the antimicrobial properties of spices than Gram-negative bacteria that did not come into contact with Gram-positive bacteria.
Read More...