.png)
In this study, the effects of different sources of serum on growing mesenchymal stem cells are compared with the goal of identifying one more suitable for clinical use.
Read More...A comparison study in the expansion of human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells
.png)
In this study, the effects of different sources of serum on growing mesenchymal stem cells are compared with the goal of identifying one more suitable for clinical use.
Read More...Conversion of Mesenchymal Stem Cells to Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts in a Tumor Microenvironment: An in vitro Study
Mesenchymal stem cells(MSCs) play a role in tumor formation by differentiating into cancer associated fibroblasts (CAFs) which enable metastasis of tumors. The process of conversion of MSCs into CAFs is not clear. In this study, authors tested the hypothesis that cancers cells secrete soluble factors that induce differentiation by culturing bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells in media conditioned by a breast cancer cell line.
Read More...Specific Transcription Factors Distinguish Umbilical Cord Mesenchymal Stem Cells From Fibroblasts
.png)
Stem cells are at the forefront of research in regenerative medicine and cell therapy. Two essential properties of stem cells are self-renewal and potency, having the ability to specialize into different types of cells. Here, Park and Jeong took advantage of previously identified stem cell transcription factors associated with potency to differentiate umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells (US-MSCs) from morphologically similar fibroblasts. Western blot analysis of the transcription factors Klf4, Nanog, and Sox2 revealed their expression was unique to US-MSCs providing insight for future methods of differentiating between these cell lines.
Read More...Wound healing properties of mesenchymal conditioned media: Analysis of PDGF, VEGF and IL-8 concentrations

Regenerative medicine has become a mainstay in recent times, and employing stem cells to treat several degenerative, inflammatory conditions has resulted in very promising outcomes. These forms of cell-based therapies are novel approaches to existing treatment modalities. In this study, the authors compared the concentrations of the cytokines PDGF, IL-8, and VEGF between conditioned and spent media of mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) to evaluate their potential therapeutic properties for wound healing in inflammatory conditions. They hypothesized that conditioned media contains higher concentrations of wound healing cytokines compared to spent media. The authors found that while IL-8 and VEGF were present in highest concentrations in conditioned media, PDGF was present in maximal amounts in spent media.
Read More...Herbal formulation, HF1 diminishes tumorigenesis: a cytokine study between MCF-7 and BM-MSCs.

The authors use HF-1, an herbal formation, on bone marrow derived cells as well as breast cancer cells to assess HF-1's ability to prevent tumorigenesis. As metastasis requires coordination of multiple cells in the tumor microenvironment, their findings that HF-1 augments cytokine expression such as VEGF & TGF-B show that HF-1 has potential application to therapeutics.
Read More...In vitro characterization of umilical cord-dervied MSC's supplemented with PLAY®:A potential FBS substitute
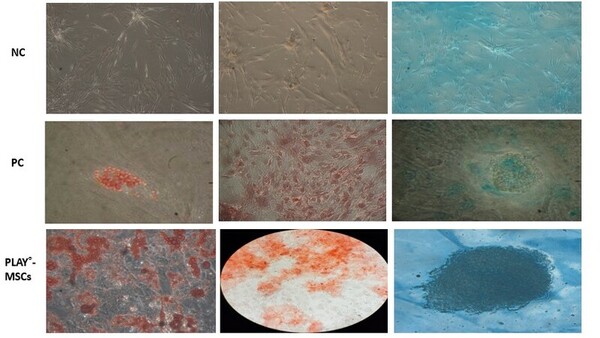
FBS is an important component in in vitro cell culture work, helping to provide needed nutrients to cells to grow. The authors look at the ability of an alternative to FBS to support cell growth in culture.
Read More...An in vitro comparative analysis of the growth factors present in FBS vs PLAY®

Here the authors performed a comparative analysis to investigate the viability of using PLAY® instead of fetal bovine serum (FBS) as a growth medium to culture cells with an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay.
Read More...Evaluation of in vitro anti-inflammatory effect of PLAY® on UC-MSCs: A COX-2 expression study
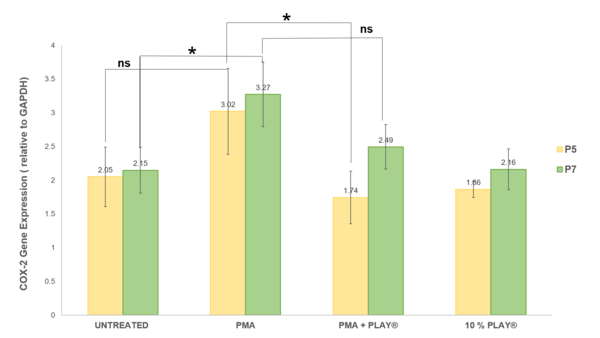
The authors seek to accelerate wound healing by reducing inflammation with a cocktail containing growth factors and bioactive modulators.
Read More...Extracellular vesicles derived from oxidatively stressed stromal cells promote cancer progression
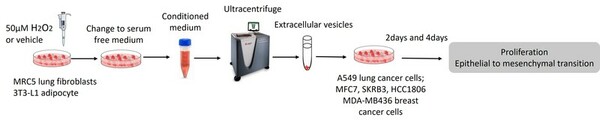
This paper hypothesized that the tumor microenvironment mediates cancer’s response to oxidative stress by delivering extracellular vesicles to cancer cells. Breast and lung cancer cells were treated with EVs, reavealing that EVs extracted from oxidatively stressed adipocytes increased the cell proliferation of breast cancer cells. These findings present a novel way that the TME influences cancer progression.
Read More...Testing the Effects of Resveratrol, Apigenin, and Glucosamine to Effectively Reduce Prostate Cancer Cell Proliferation, Migration Levels, and Increase Apoptosis
The current five-year survival rate of metastasized prostate cancer is only 30% and occurs in every one in nine men. Researchers have shown that people with a type of dwarfism called Laron’s Syndrome are immune to cancer due to their low levels of insulin-like growth factor-1 (IGF-1). For this reason, experimentally modifying the level of IGF-1 could provide better insight into whether lowering the levels of IGF-1 in prostate cancer cell lines (e.g. PC-3) could be an effective treatment to reduce their rates of proliferation and migration and increase apoptosis. We selected three compounds, which researchers have shown decrease IGF-1 levels, to test and combine to determine which is the most promising.
Read More...