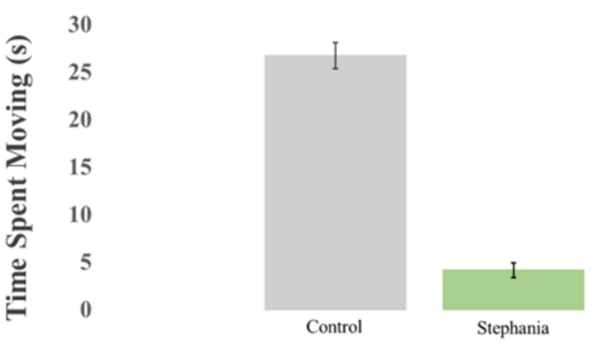
In this study the authors looked at the extract of Stephania tetrandra and its impact on symptoms related to obsessive compulsive disorder in fruit flies.
Read More...Administration of Stephania tetrandra to Drosophila melanogaster to create obsessive compulsive disorder model

In this study the authors looked at the extract of Stephania tetrandra and its impact on symptoms related to obsessive compulsive disorder in fruit flies.
Read More...Impact of gadodiamide (Omniscan) on a beef liver catalase ex vivo model
Here, seeking to better understand the effects of gadolinium-based contrast agents, dyes typically used for MRI scans, the authors evaluated the activity of catalase found in beef liver both with and without gadodiamide when exposed to hydrogen peroxide. They found that gadioamide did not significantly inhibit catalase's activity, attributing this lack of effects to the chelating agent found in gadodiamide.
Read More...Pediatric probiotic culture survival study in acidic pH using an in vitro model
In this study, the authors investigate the effects of acidity on the survival of commercial probiotic Lovebug bacterial strains.
Read More...Modelling effects of alkylamines on sea salt aerosols using the Extended Aerosols and Inorganics Model

With monitoring of climate change and the evolving properties of the atmosphere more critical than ever, the authors of this study take sea salt aerosols into consideration. These sea salt aerosols, sourced from the bubbles found at the surface of the sea, serve as cloud condensation nuclei (CCN) and are effective for the formation of clouds, light scattering in the atmosphere, and cooling of the climate. With amines being involved in the process of CCN formation, the authors explore the effects of alkylamines on the properties of sea salt aerosols and their potential relevance to climate change.
Read More...Transfer Learning for Small and Different Datasets: Fine-Tuning A Pre-Trained Model Affects Performance
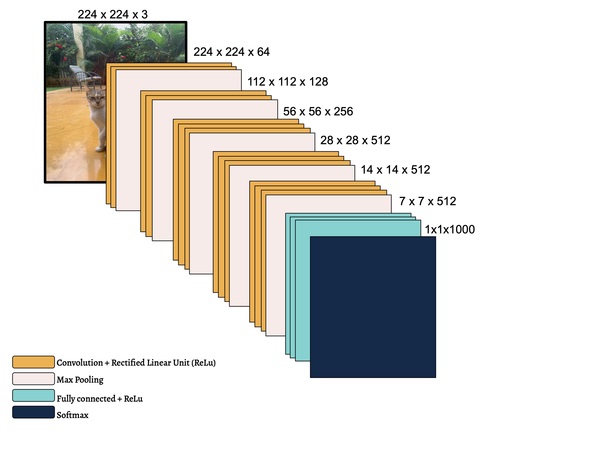
In this study, the authors seek to improve a machine learning algorithm used for image classification: identifying male and female images. In addition to fine-tuning the classification model, they investigate how accuracy is affected by their changes (an important task when developing and updating algorithms). To determine accuracy, a set of images is used to train the model and then a separate set of images is used for validation. They found that the validation accuracy was close to the training accuracy. This study contributes to the expanding areas of machine learning and its applications to image identification.
Read More...The Effects of Ezetimibe on Triglyceride and Alanine Transaminase Reduction in Drosophila Melanogaster Model of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD)
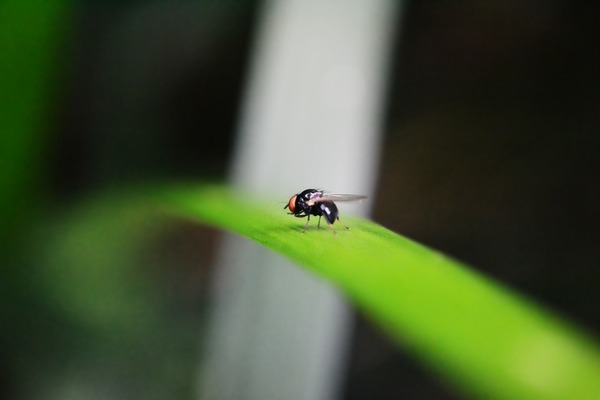

Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) is a condition where a surplus of triglycerides or fat are present in the liver. In this study, ezetimibe, a cholesterol lowering drug, was used to treat flies modeling NAFLD. Compared to the coconut oil fed flies that were transferred to the control medium, the flies transferred to the control medium treated with ezetimibe showed a decrease in their triglyceride and alanine transaminase level.
Read More...The Effect of Antioxidant Vitamins on Mustard Plants in a Hydrogen Peroxide-Induced Injury Model
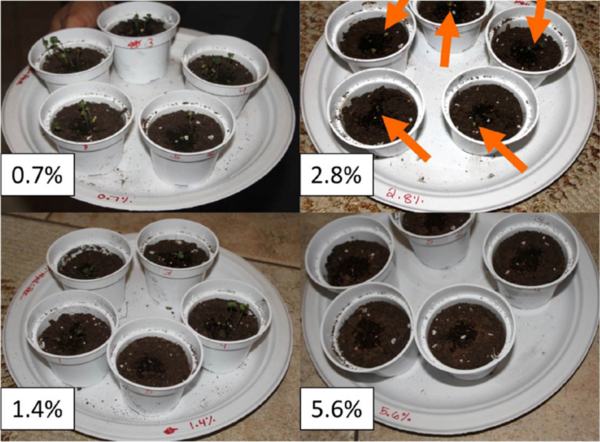

In this study, the authors assess the antioxidant properties of vitamins A, C and E given to mustard plants after oxidative damage. This research shows an interesting comparison of the vitamins' effect on plant recovery and health.
Read More...Temperature and Precipitation Responses to a Stratospheric Aerosol Geoengineering Experiment Using the Community Climate System Model 4
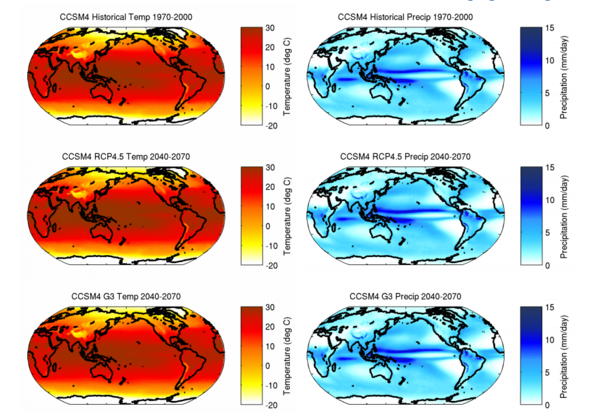
We are changing our environment with steadily increasing carbon dioxide emissions, but we might be able to help. The authors here use a computer program called Community Climate System Model 4 to predict the effects of spraying small particles into the atmosphere to reflect away some of the sun's rays. The software predicts that this could reduce the amount of energy the Earth's atmosphere absorbs and may limit but will not completely counteract our carbon dioxide production.
Read More...Stock price prediction: Long short-term memory vs. Autoformer and time series foundation model
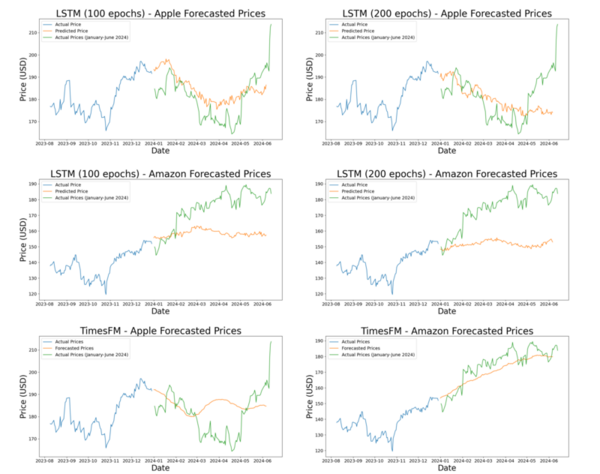
The authors looked the ability to predict future stock prices using various machine learning models.
Read More...Exposure to Schistosoma mansoni antigen induces an allergic response to peanuts in an American cockroach model
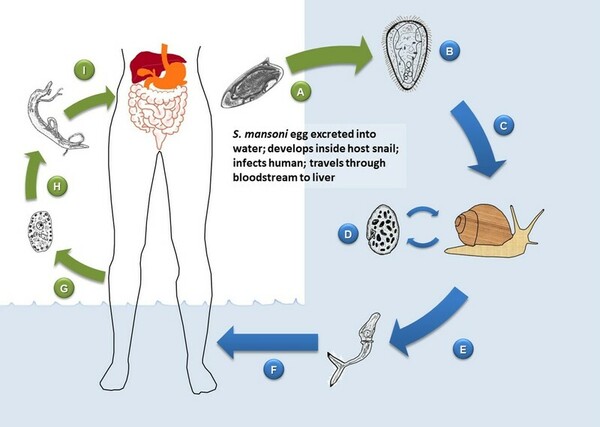
Pillai et al. look at whether exposure to Schistosoma mansoni, a parasitic blood fluke, has any relation to peanut allergies. They found that cockroaches exposed to an antigen found in S. mansoni eggs exhibited an allergic reaction to peanuts.
Read More...