
The authors looked at the impacts of short-chain fatty acids on muscle fiber formation as well as insulin sensitivity using a model of mouse myoblasts.
Read More...Investigating the impact of short-chain fatty acids on myofiber dynamics and insulin sensitivity

The authors looked at the impacts of short-chain fatty acids on muscle fiber formation as well as insulin sensitivity using a model of mouse myoblasts.
Read More...Elevated GPx4 and FSP1 expression in MG63 cells: Exploring potential links to drug resistance and ferroptosis
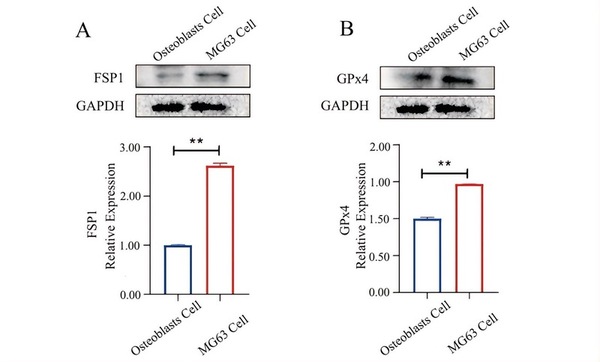
Current osteosarcoma (OS) treatments rely on surgery and chemotherapy, but drug resistance remains a major challenge that lowers patient survival rates. Ferroptosis, a form of regulated cell death, has shown promise in cancer therapy but is not well understood in OS. This study explores the use of Ferroptosis in OS.
Read More...Comparison of total flavonoid content and DPPH● sequestration in Arabica, Robusta, and Liberica coffee beans

Here the authors used a free radical assay to characterize the antioxidant capacity of three types of coffee beans. They fond that Robusta coffee presented greater inhibition percentages than other species in their free radical assay, indicating higher antioxidant capacity.
Read More...Computational analysis and drug repositioning: Targeting the TDP-43 RRM using FDA-approved drugs
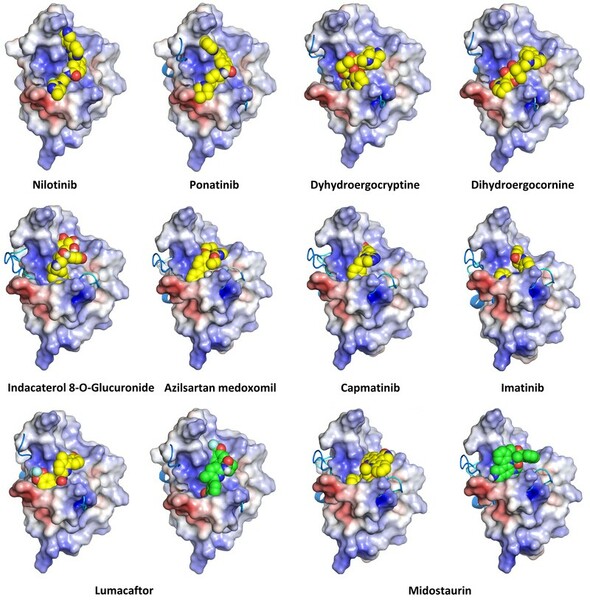
Molecules which bind to proteins that aggregate abnormally in neurodegenerative diseases could be promising drugs for these diseases. In this study, Zhang, Wu, Zhang, and Dang simulate the binding behavior of various molecules to screen for candidates which could be promising candidates for drug development.
Read More...Association between nonpharmacological interventions and dementia: A retrospective cohort study

Here, the authors investigated the role of nonpharmacological interventions in preventing or delaying cognitive impairment in individuals with and without dementia. By using a retrospective case-control study of 22 participants across two senior centers in San Diego, they found no significant differences in self-reported activities. However, they found that their results reflected activity rather than the activity itself, suggesting the need for an alternative type of study.
Read More...Modular mimics of neuroactive alkaloids - design, synthesis, and cholinesterase inhibitory activity of rivastigmine analogs
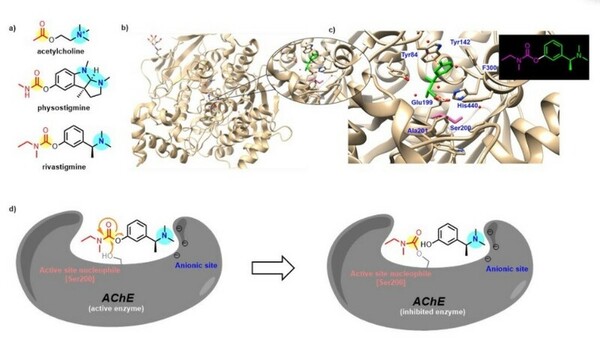
Naturally occurring neuroactive alkaloids are often studied for their potential to treat Neurological diseases. This team of students study Rivastigmine, a potent cholinesterase inhibitor that is a synthetic analog of physostigmine, which comes from the Calabar bean plant Physostigma venenosum. By comparing the effects of optimized synthetic analogs to the naturally occurring alkaloid, they determine the most favorable analog for inhibition of acetylcholinesterase (AChE), the enzyme that breaks down the neurotransmitter acetylcholine (ACh) to terminate neuronal transmission and signaling between synapses.
Read More...Assessing CDK5 as a Nanomotor for Chemotactic Drug Delivery
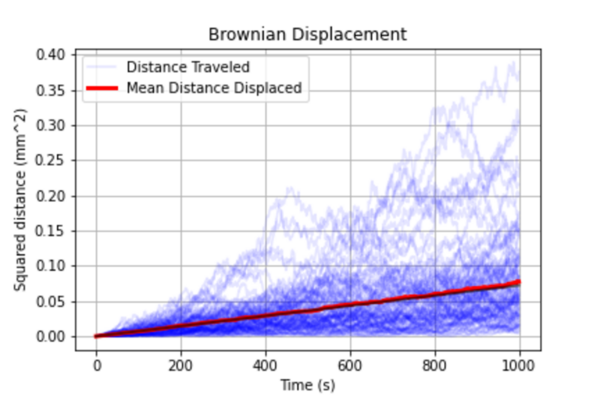
Enzyme chemotaxis is a thermodynamic phenomenon in which enzymes move along a substrate concentration gradient towards regions with higher substrate concentrations and can be used to steer nanovehicles towards targets along natural substrate concentrations. In patients with Alzheimer’s disease, a gradient of tau protein forms in the bloodstream. Tau protein is a substrate of the enzyme CDK5, which catalyzes the phosphorylation of tau protein and can travel using chemotaxis along tau protein gradients to increasing concentrations of tau and amyloid-beta proteins. The authors hypothesized that CDK5 would be able to overcome these barriers of Brownian motion and developed a quantitative model using Michaelis-Menten kinetics to define the necessary parameters to confirm and characterize CDK5’s chemotactic behavior to establish its utility in drug delivery and other applications.
Read More...Development of Diet-Induced Insulin Resistance in Drosophila melanogaster and Characterization of the Anti-Diabetic Effects of Resveratrol and Pterostilbene

Dhar and colleagues established a Type II diabetes mellitus (T2DM) model in fruit flies, using this model to induce insulin resistance and characterize the effects Resveratrol and Pterostilbene on a number of growth and activity metrics. Resveratrol and Pterostilbene treatment notably overturned the weight gain and glucose levels. The results of this study suggest that Drosophila can be utilized as a model organism to study T2DM and novel pharmacological treatments.
Read More...Investigating toxicity and antimicrobial properties of silver nanoparticles in Escherichia coli and Drosophila melanogaster
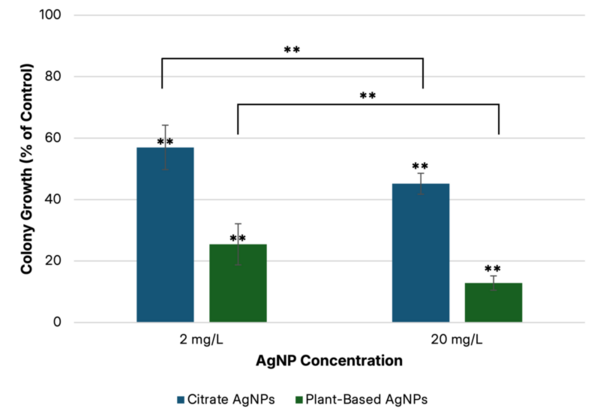
This paper looks at the antibacterial and toxic effects of silver nanoparticles (AgNPs) on Escherichia coli bacteria and Drosophila melanogaster fruit flies. They modified the AgNPs size, concentration, and surface coating to determine the effects on each of the organisms. For both organisms, increased AgNP concentration demonstrated increased toxicity but particle size and surface coating had opposing effects.
Read More...Quantifying natural recovery of dopamine deficits induced by chronic stress
Here the authors investigated the natural recovery of stress-induced dopamine-related gene deficits in C. elegans by measuring the expression of cat-2 (dopamine biosynthesis) and sod-2 (oxidative stress) following exposure to starvation or hydrocortisone. They found that the reversibility of sod-2 and the expression of cat-2 were highly dependent on the type and severity of the stressor, suggesting that the body's natural ability to recover from dopamine dysfunction has biological limitations.
Read More...