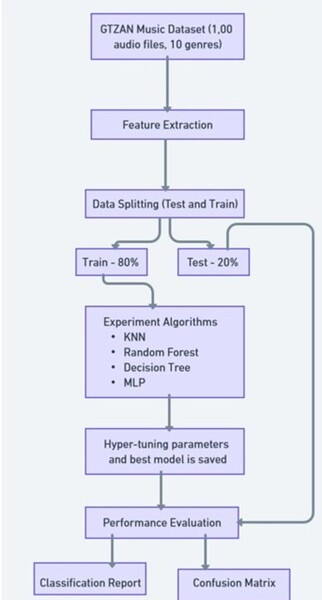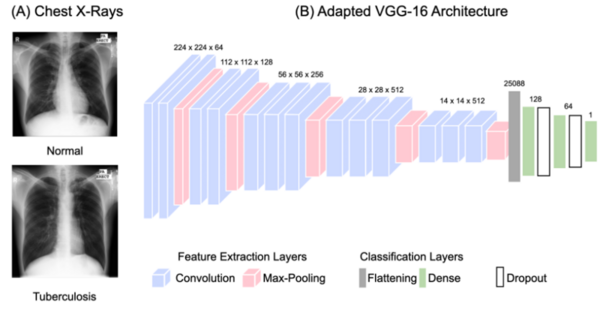
Here, beginning from an initial interest in the possibility to use a computer to automatically solve a geometry diagram parser, the authors developed their own Fast Geometry Diagram Parser (FastGDP) that uses clustering and corner information. They compared their own methods to a more widely available, method, GeoSolver, finding their own to be an order of magnitude faster in most cases that they considered.
Read More...