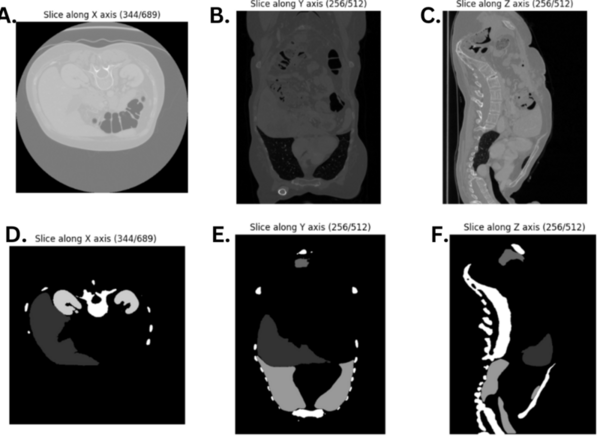
The authors looked at different models of semantic segmentation to determine which may be best used in the future for segmentation of CT scans to help diagnose certain conditions.
Read More...Unlocking robotic potential through modern organ segmentation

The authors looked at different models of semantic segmentation to determine which may be best used in the future for segmentation of CT scans to help diagnose certain conditions.
Read More...Synthesis of sodium alginate composite bioplastic films

The authors looked at the development of biodegradable bioplastic and its features compared to PET packaging films. They were able to develop a biodegradable plastic with sodium alginate that dissolved in water and degrade in microbial conditions while also being transparent and flexible similar to current plastic films.
Read More...Optical anisotropy of crystallized vanillin thin film: the science behind the art
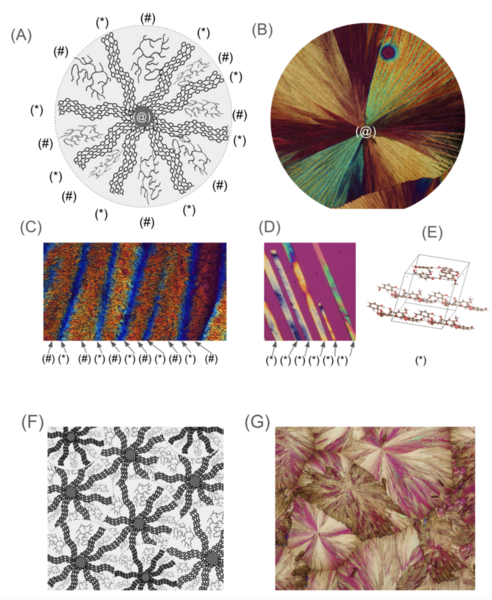
Microscopic beauty is hiding in common kitchen ingredients - even vanillin flavoring can be turned into mesmerizing artwork by crystallizing the vanillin and examining it under a polarizing microscope. Wang and Pang explore this hidden beauty by determining the optimal conditions to grow crystalline vanillin films and by creating computer simulations of chemical interactions between vanillin molecules.
Read More...Pressure and temperature influence the efficacy of metal-organic frameworks for carbon capture and conversion
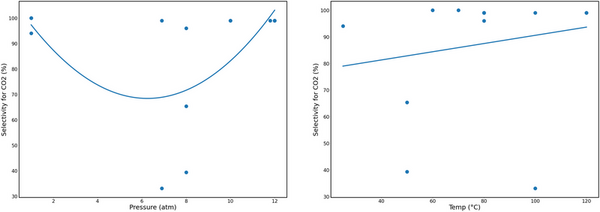
Metal-organic frameworks (MOFs) are promising new nanomaterials for use in the fight against climate change that can efficiently capture and convert CO2 to other useful carbon products. This research used computational models to determine the reaction conditions under which MOFs can more efficiently capture and convert CO2. In a cost-efficient manner, this analysis tested the hypothesis that pressure and temperature affect the efficacy of carbon capture and conversion, and contribute to understanding the optimal conditions for MOF performance to improve the use of MOFs for controlling greenhouse CO2 emissions.
Read More...Analyzing resilience in a sample population as a novel qualifier for triage in psychological first aid

While serving as an immediate address for psychological safety and stability, psychological first aid (PFA) currently lacks the incorporation of triage. Without triage, patients cannot be prioritized in correspondence to condition severity that is often called for within emergency conditions. To disentangle the relevance of a potential triage system to PFA, the authors of this paper have developed a method to quantify resilience - a prominent predictor of the capability to recover from a disaster. With this resilience index, they have quantified resilience of differing age, race, and sex demographics to better inform the practice of PFA and potential demographic prioritization via a triage system.
Read More...The role of xpa-1 and him-1 in UV protection of Caenorhabditis elegans
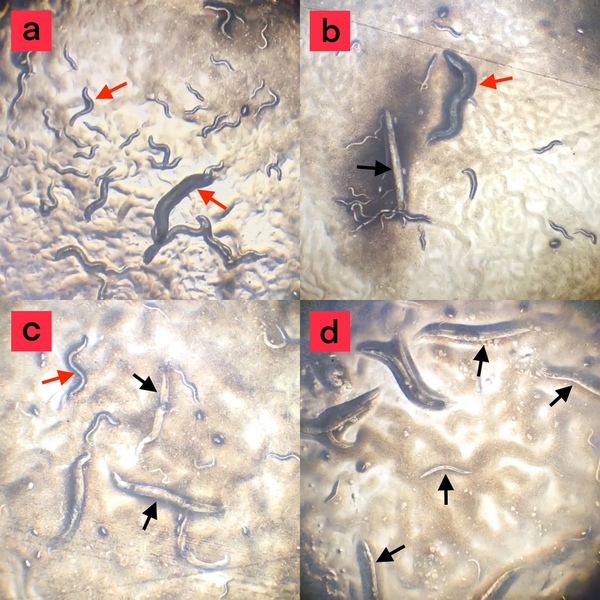
Caenorhabditis elegans xpa-1 and him-1 are orthologs of human XPA and human SMC1A, respectively. Mutations in the XPA are correlated with Xeroderma pigmentosum, a condition that induces hypersensitivity to ultraviolet (UV) radiation. Alternatively, SMC1A mutations may lead to Cornelia de Lange Syndrome, a multi-organ disorder that makes patients more sensitive to UVinduced DNA damage. Both C. elegans genes have been found to be involved in protection against UV radiation, but their combined effects have not been tested when they are both knocked down. The authors hypothesized that because these genes are involved in separate pathways, the simultaneous knockdown of both of these genes using RNA interference (RNAi) in C. elegans will cause them to become more sensitive to UV radiation than either of them knocked down individually. UV protection was measured via the percent survival of C. elegans post 365 nm and 5.4x10-19 joules of UV radiation. The double xpa-1/him-1 RNAi knockdown showed a significantly reduced percent survival after 15 and 30 minutes of UV radiation relative to wild-type and xpa-1 and him-1 single knockdowns. These measurements were consistent with their hypothesis and demonstrated that xpa-1 and him-1 genes play distinct roles in resistance against UV stress in C. elegans. This result raises the possibility that the xpa-1/him-1 double knockdown could be useful as an animal model for studying the human disease Xeroderma pigmentosum and Cornelia de Lange Syndrome.
Read More...Ribosome distribution affects stalling in amino-acid starved cancer cells
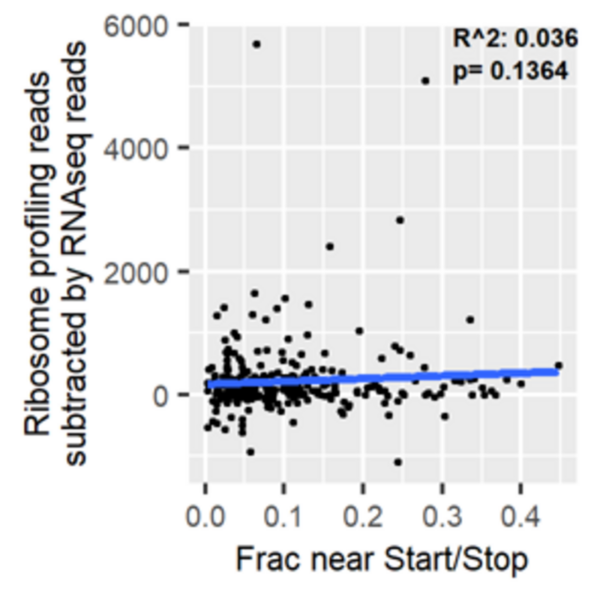
In this article, the authors analyzed ribosome profiling data from amino acid-starved pancreatic cancer cells to explore whether the pattern of ribosome distribution along transcripts under normal conditions can predict the degree of ribosome stalling under stress. The authors found that ribosomes in amino acid-deprived cells stalled more along elongation-limited transcripts. By contrast, they observed no relationship between read density near start and stop and disparities between mRNA sequencing reads and ribosome profiling reads. This research identifies an important relationship between read distribution and propensity for ribosomes to stall, although more work is needed to fully understand the patterns of ribosome distribution along transcripts in ribosome profiling data.
Read More...The Long-Term Effect of CBD Crystals and CBD Oil on Depressive-Associated Rat Behaviors

Cannabidiol (CBD) is a chemical extracted from cannabis and shown by some studies to alleviate the symptoms of many mental disorders, especially major depressive disorder. The authors hypothesized that chronic treatments with purified CBD through oral administration would relieve depression-associated behaviors in normal healthy rats under adverse conditions. A statistical analysis of the experimental data suggested that long-term consumption of CBD could elicit depression associated symptoms in normal rats without depression. The results imply that people should consume CBD-containing products with extreme caution and highlight the need to carefully monitor the use of CBD in health care products.
Read More...Harvesting Atmospheric Water
The objective of this project was to test various materials to determine which ones collect the most atmospheric water when exposed to the same environmental factors. The experiment observed the effect of weather conditions, a material’s surface area and hydrophilicity on atmospheric water collection. The initial hypothesis was that hydrophobic materials with the greatest surface area would collect the most water. The materials were placed in the same outside location each night for twelve trials. The following day, the materials were weighed to see how much water each had collected. On average, ribbed plastic collected 10.8 mL of water per trial, which was over 20% more than any other material. This result partially supported the hypothesis because although hydrophobic materials collected more water, surface area did not have a significant effect on water collection.
Read More...The Impacts of Varying Types of Light on the Growth of Five Arabidopsis Varieties

Arabadopsis, “the fruit fly of plants”, is an easy to grow plant system for genetic manipulation. Here, researchers tested the effects of varied light conditions on plants with specific mutations in the light sensing pathways.
Read More...