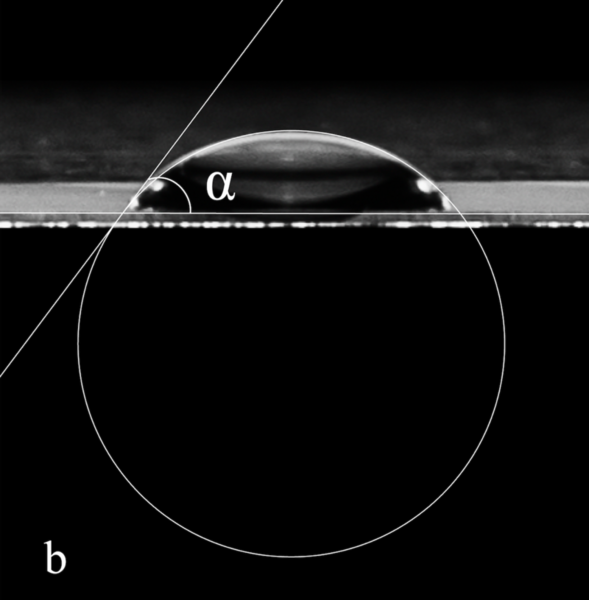
In healthy ecosystems, organisms interact in a relationship that helps maintain one another's existence. Stress can disrupt this interaction, compromising the survival of some of the members of such relationships. Here, the authors investigate the effect of stress on the interaction between anemones and their microbiome. Their study suggests that stress changes the composition of the surface microbiome of the anemone D. lineata, which is accompanied by an increase in mucus secretion. Future research into the composition of this stress-induced mucus might reveal useful antimicrobial properties.
Read More...