Solubility of graphite and the efficacy of using its dissolved form as a conductive paste
(1) Summer Ventures in Science and Mathematics
https://doi.org/10.59720/23-237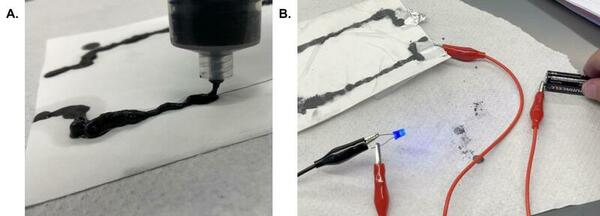
Graphite is an inexpensive, common, and environmentally friendly compound with many unique properties, one being conductivity. With the world becoming more dependent on electricity, conductive materials have become increasingly relevant, and with them, graphite. This study aimed to take advantage of graphite's conductivity to evaluate its efficacy for use in circuit boards and other applications by using the solution resulting from exfoliation as a conductive paste. We hypothesized that using organic solvents and physical agitation in the form of sonication would increase the solubility of graphite and the solution's overall conductivity. Specifically, we hypothesized that sonication would interfere with enough of the π-stacking interactions to increase the surface area and conductivity of the solute, and the organic solvents would allow for a more consistent dispersion of the graphite solute than water due to graphite's hydrophobic nature. Dissolving graphite in acetone combined with sonication was the most successful method of creating a conductive paste because the solution that was created maintained a high conductivity and had other favorable properties such as a low boiling point (and thus a quicker evaporation time). We found that using a conductive paste for a customizable circuit could be practical as long as a few key engineering challenges are met—mainly, protecting the paste from the external environment and making good connections to the coating. This paste may not replace wires, but as a result of its properties, could have many future uses in the field of electronics or even infrastructure.
This article has been tagged with: