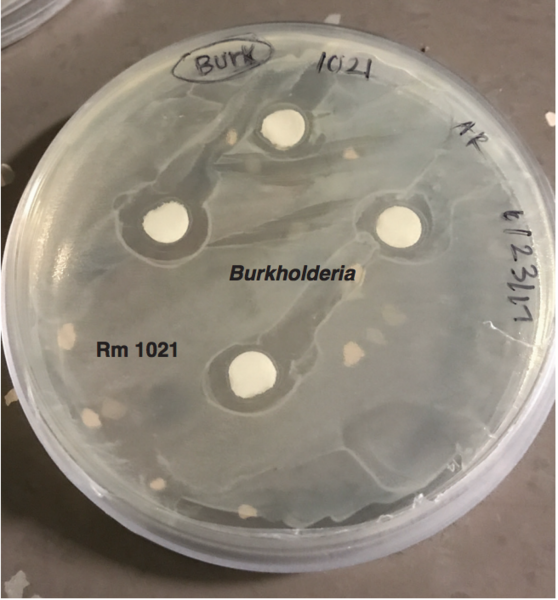
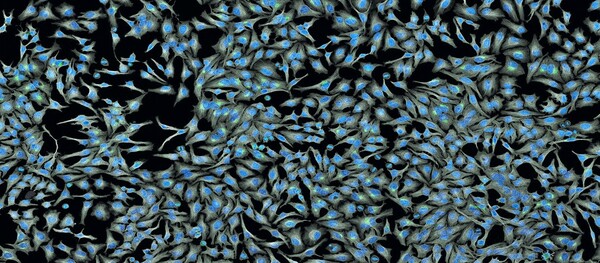
Kashyap Jha et al. look at the formulation of MAT20, a crude extract of the moringa, amla, and tulsi leaves, as a potential complementary and alternative medicine. Using HeLa cells, they find MAT20 up-regulates expression of inflammation and cell cytotoxicity markers. Their data is important for understanding the anti-cancer and anti-inflammatory properties of MAT20.
Read More...