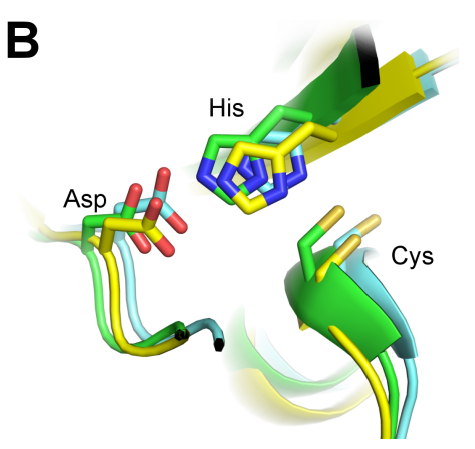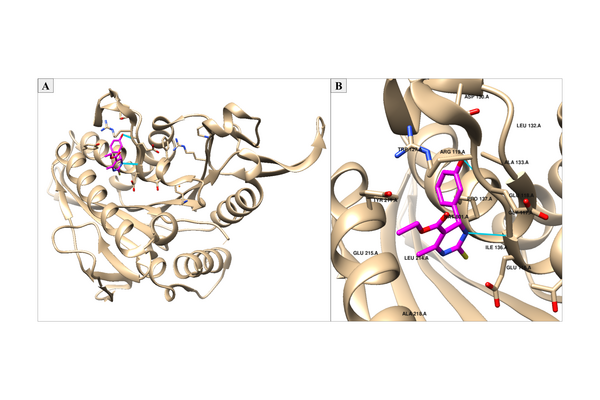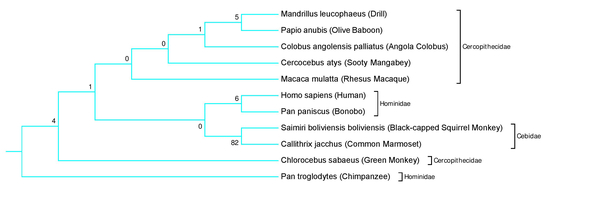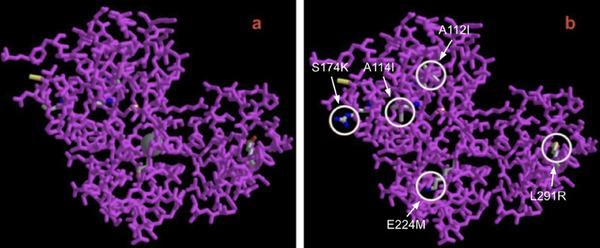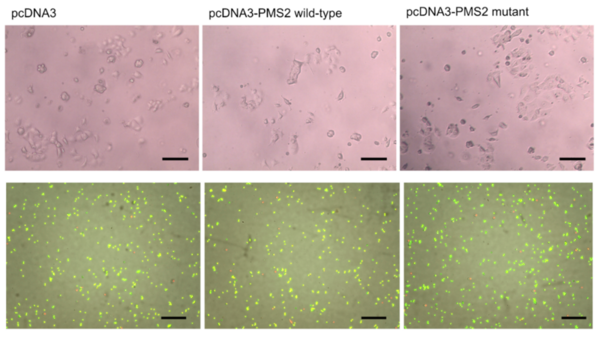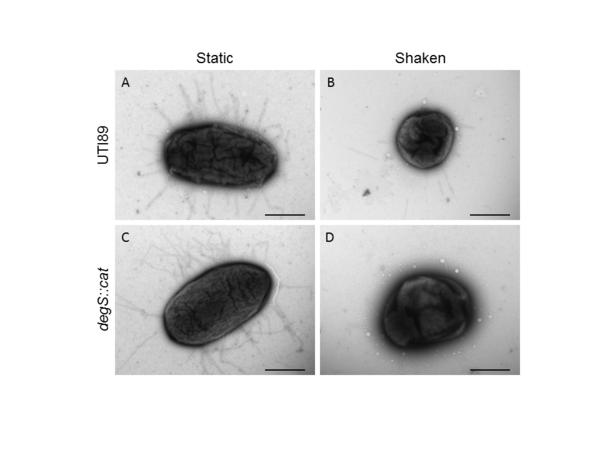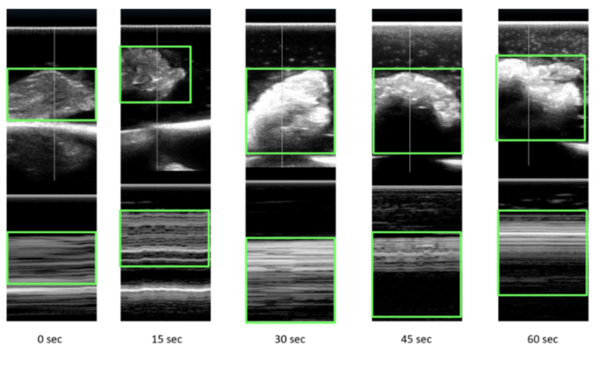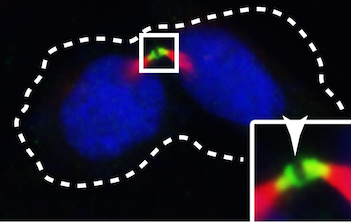
In order for cells to successfully multiply, a number of proteins are needed to correctly coordinate the replication and division process. In this study, students use fluorescence microscopy and molecular methods to study CCDC11, a protein critical in the formation of cilia. Interestingly, they uncover a new role for CCDC11, critical in the cell division across multiple human cell lines.
Read More...