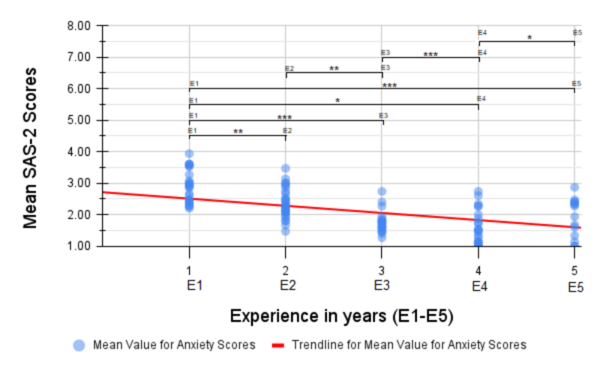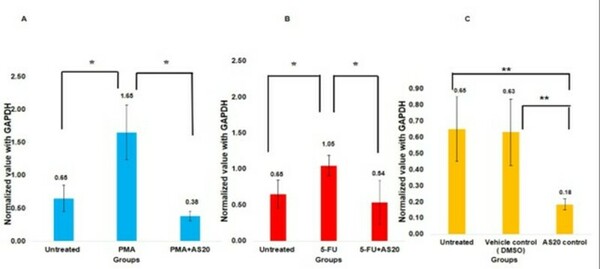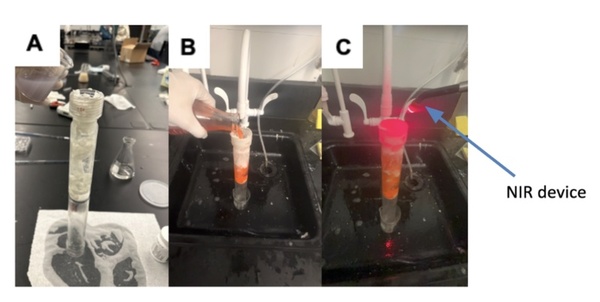
Coronary artery disease, the leading cause of death worldwide, results from cholesterol build-up in coronary arteries, limiting blood and oxygen flow to the heart. This study investigated the use of gold and silver nanoparticles coated with aspirin and activated by near-infrared light to improve blood flow in a clogged artery model. The nanoparticles increased simulated blood flow rates, demonstrating potential as a less invasive and more targeted treatment for cardiovascular disease.
Read More...