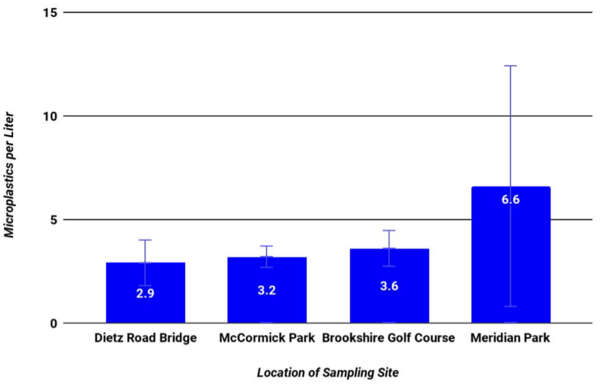
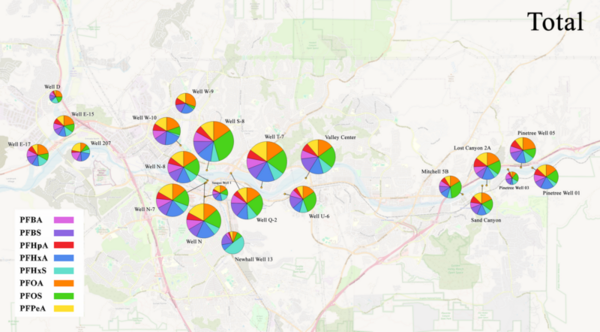
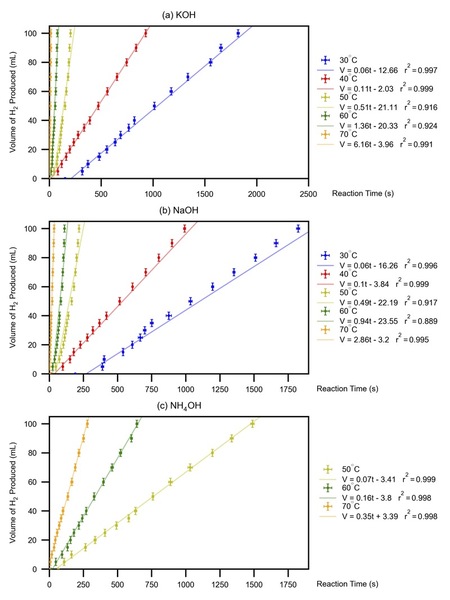
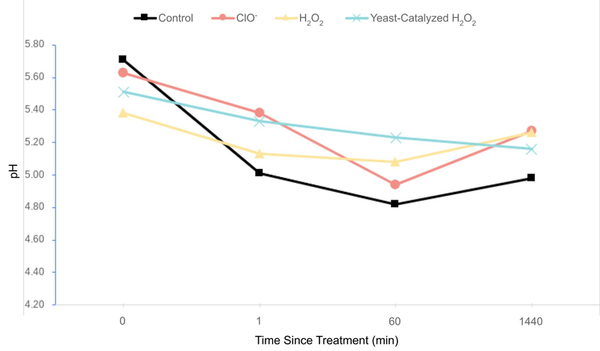
Industrialization has transformed human life and improved it for many. Nonetheless, a side effect has been an increase in chemical waste, which when not disposed of properly, has detrimental effects on surrounding habitats. An increase in ocean acidification could potentially affect many forms of life, disrupting the ecological balance in unforeseeable ways. In this article the authors explore the effect of acidification on corals and shells, and observe that an increase in ocean acidity has a significant effect on corals, but not shells. This illustrates how acidification could negatively affect marine life, and calls our attention to managing the factors that contribute to increasing the pH of the Earth's water bodies.
Read More...