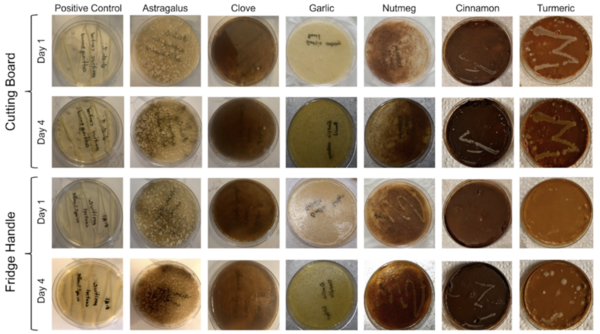
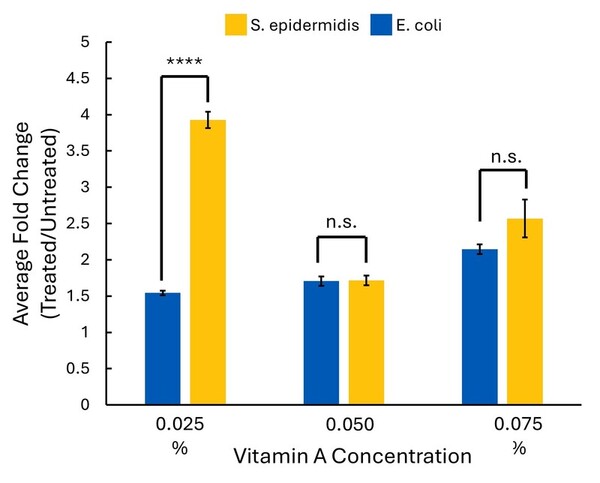
Here, the authors sought to use Cladophora macroalgae as a possible antibiotic to address the growing threat of antibiotic resistance in pathogenic bacteria. However, when they observed algae extracts to be greatly contaminated with gram-negative bacteria, they adapted to explore the ability to use ultraviolet light as a bactericide. They found that treatment with ultraviolet light had a significant effect.
Read More...