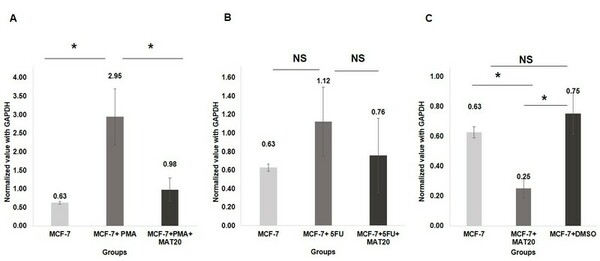
The authors test potential anti-inflammatory and pro-apoptotic effects of a polyherbal extract formulation on cultured breast cancer cells.
Read More...Anti-inflammatory and pro-apoptotic properties of the polyherbal drug, MAT20, in MCF-7 cells

The authors test potential anti-inflammatory and pro-apoptotic effects of a polyherbal extract formulation on cultured breast cancer cells.
Read More...Virtual Screening of Cutibacterium acnes Antibacterial Agent Using Natural Compounds Database
A common form of Acne is caused by a species of bacterium called Cutibacterium acnes. By using a predictive algorithm and structural analysis, the authors identified 5 small molecules with high affinity to growth factors in Catibacterium acnes. This has potential implications for supplemental skincare products.
Read More...Formulation of novel polyherbal compound MAT20 with phytochemicals found in amla, tulsi, and moringa

With herbal plants providing an address to the adverse effects of oxidative stress found within the body, the authors of this article develop and assess a novel compound (“MAT20”) that blends three herbal plants for optimal oxidative stress relief.
Read More...Phytochemical analysis of Annona Reticulata extract and an in-vitro study on its anti-proliferative effects
In this study, the authors investigate the anti-cancer effects of Annona Reticulata (Ramphal or custard apple) by testing whether its extract could inhibit HeLa cell viability.
Read More...Alkaloids Detection in Commonly Found Medicinal Plants with Marquis Reagent

This study investigates the presence of alkaloids in a variety of medicinal plants using the Marquis reagent. They reveal some surprising results and how useful the Marquis reagent is.
Read More...The Effect of Neem on Common Nosocomial Infection-Causing Organisms

Nosocomial infections acquired in hospitals pose a risk to patients, a risk compounded by resistant microorganisms. To combat this problem, researchers have turned to bioactive compounds from medicinal plants such as the widely used neem. In the present study, researchers sought to determine the effectiveness of different neem preparations against several hospital acquired human pathogens. Neem powder in water successfully inhibited microorganism growth making it a potential agent to combat these infections.
Read More...Allelopathic Effects of Kudzu (Pueraria montana) on Seed Germination and Their Potential Use As a Natural Herbicide
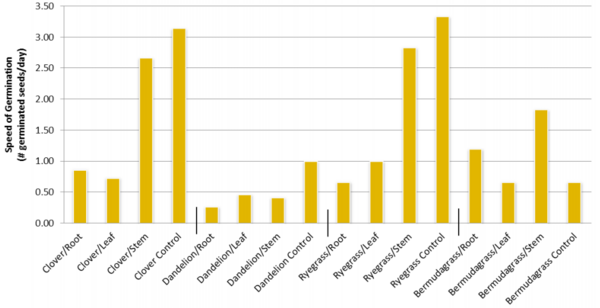
Plants in the wild compete with each other for nutrients and sunlight. Kudzu is a weed that is thought to secrete compounds that inhibit the growth of other plants. Here the authors find that certain parts of kudzu plants can block the germination of clover and dandelion seeds. These experiments may lead to a weed killer that is safe and naturally derived.
Read More...Investigating the anticancer effects of Uvularia perfoliata
This paper investigates the potential anticancer properties of Uvularia perfoliata by testing its effects on the viability of uveal melanoma cells.
Read More...Anticancer, anti-inflammatory, and apoptotic activities of MAT20, a poly-herbal formulation.

Kashyap Jha et al. look at the formulation of MAT20, a crude extract of the moringa, amla, and tulsi leaves, as a potential complementary and alternative medicine. Using HeLa cells, they find MAT20 up-regulates expression of inflammation and cell cytotoxicity markers. Their data is important for understanding the anti-cancer and anti-inflammatory properties of MAT20.
Read More...Feature extraction from peak detection algorithms for enhanced EMG-based hand gesture recognition models
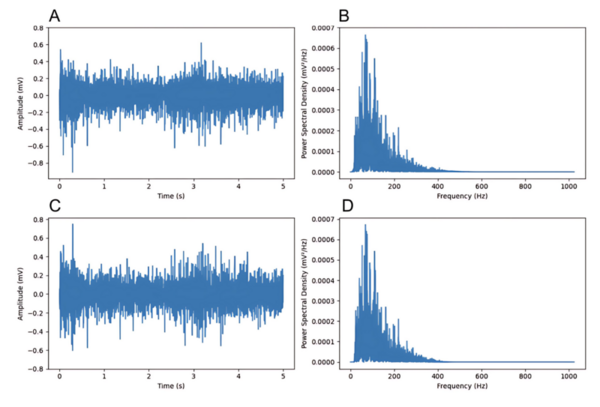
This manuscript evaluates peak detection algorithms for feature extraction in EMG-based hand gesture recognition using a random forest classifier. The study demonstrates that wavelet-based peak detection features achieve the highest classification accuracy (96.5%), outperforming other methods. The results highlight the potential of peak features to improve EMG-based prosthetic control systems.
Read More...