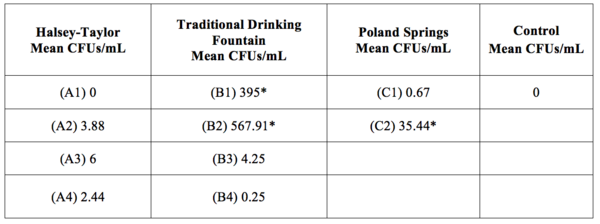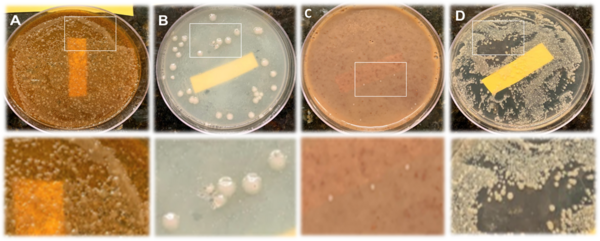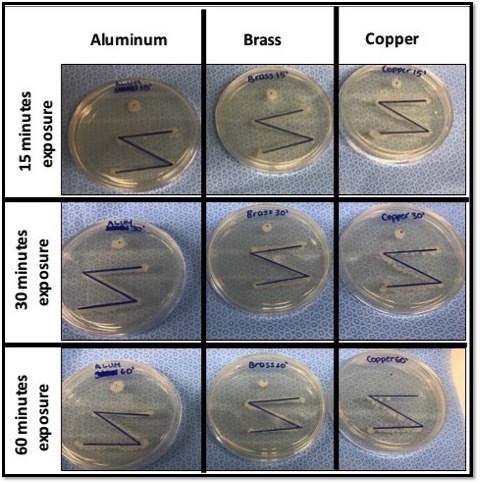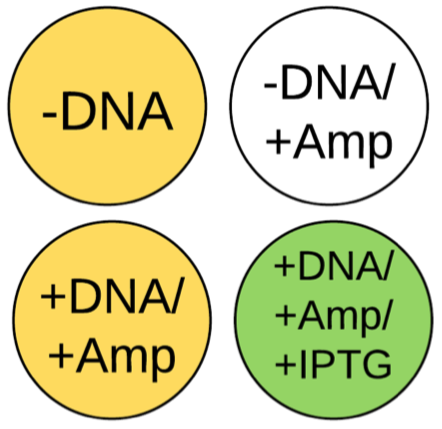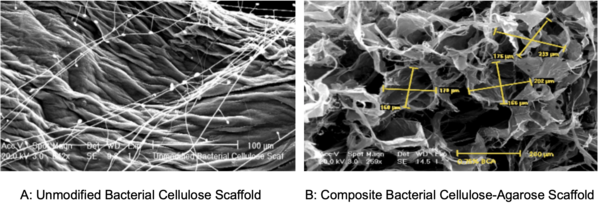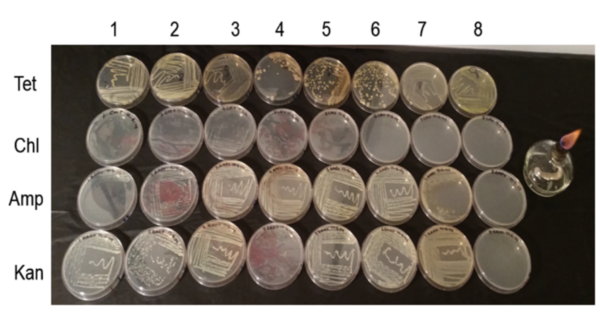
The emergence of antibiotic-resistant pathogenic bacteria is a major concern for human health, rendering some antibiotics ineffective in treating diseases. The authors of this study tested the hypothesis that exposing rumen bacteria to tetracycline will gradually lead to the development of tetracycline-resistant bacteria, some of which will develop multidrug resistance.
Read More...