The authors investigated prophages present in Streptococcus bacteria that may increase their survival in different environments.
Read More...Distribution of prophages in the Streptococcus bacteria genus and their role in increasing host pathogenicity

The authors investigated prophages present in Streptococcus bacteria that may increase their survival in different environments.
Read More...Significance of Tumor Growth Modeling in the Behavior of Homogeneous Cancer Cell Populations: Are Tumor Growth Models Applicable to Both Heterogeneous and Homogeneous Populations?
This study follows the process of single-cloning and the growth of a homogeneous cell population in a superficial environment over the course of six weeks with the end goal of showing which of five tumor growth models commonly used to predict heterogeneous cancer cell population growth (Exponential, Logistic, Gompertz, Linear, and Bertalanffy) would also best exemplify that of homogeneous cell populations.
Read More...Paralyzing effects of CO2 and hypothermia on Madagascar hissing and dubia cockroaches

Here the authors sought to find a more ethical and efficient way to temporary paralyze a cockroach by comparing the results of two methods. By comparing immobilization through immersion in cold water and exposure to a 100 % CO2 environment, they found that cockroaches could be immobilized and recovered significantly faster when exposed to CO2.
Read More...pH-dependent drug interactions with acid reducing agents
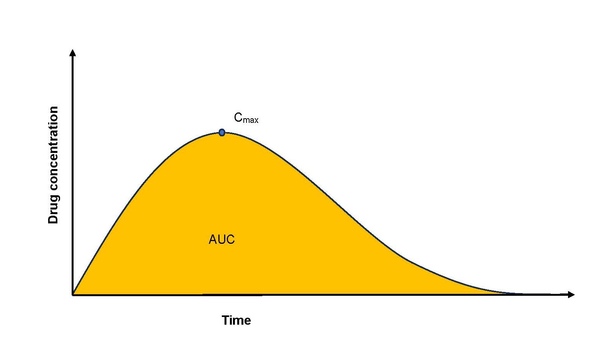
Some cancer treatments lose efficacy when combined with treatments for excessive stomach acid, due to the changes in the stomach environment caused by the stomach acid treatments. Lin and Lin investigate information on oral cancer drugs to see what information is available on interactions of these drugs.
Read More...Nature’s reset: The effect of native and invasive plant forage on honey bee nutrition and survival
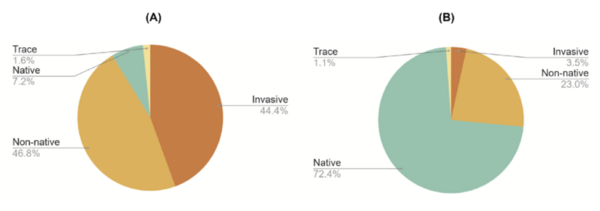
The authors looked at survival of honey bees over the winter in regards to native and invasive plant availability. They found that native plants provided greater survivability and overall health compared to environments where there was an abundance of invasive plants.
Read More...Access to public parks, drinking fountains, and clean public drinking water in the Bay Area is not driven by income

Access to green space—an area of grass, trees, or other vegetation set apart for recreational or aesthetic purposes in an urban environment—and clean drinking water can be unequally distributed in urban spaces, which are often associated with income inequality. Little is known about public drinking water and green space inequities in the Bay Area. For our study, we sought to understand how public park access, drinking fountain access, and the quality of public drinking water differ across income brackets in the Bay Area. Though we observed smaller-scale instances of inequalities, in the park distribution in the Bay Area as a whole, and in the Southern Bay’s water quality and park distribution, our results indicate that other factors could be influencing water quality, and park and fountain access in the Bay Area.
Read More...Assessing Attitude Across Different Age Groups in Regard to Global Issues: Are Kids More Optimistic Than Adults?
In this article the authors investigate whether there is a correlation between age of a person and their outlook on global issues such as technology, politics, and environment. They find a correlation between increased age and decreased optimism. However regardless of age, they find that respondents believe certain characteristics such as technology and willingness to change are essential for improvements.
Read More...Testing Various Synthetic and Natural Fiber Materials for Soundproofing
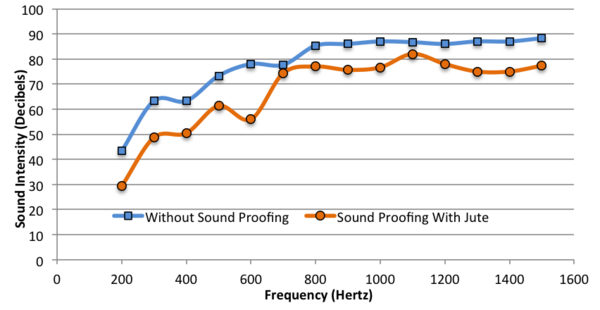
Noise pollution negatively impacts the health and behavioral routines of humans and other animals, but the production of synthetic sound-absorbing materials contributes to harmful gas emissions into the atmosphere. The authors of this paper investigated the effectiveness of environmentally-friendly, cheap natural-fiber materials, such as jute, as replacements for synthetic materials, such as gypsum and foam, in soundproofing.
Read More...Efficient synthesis of superabsorbent beads using photopolymerization with a low-cost method
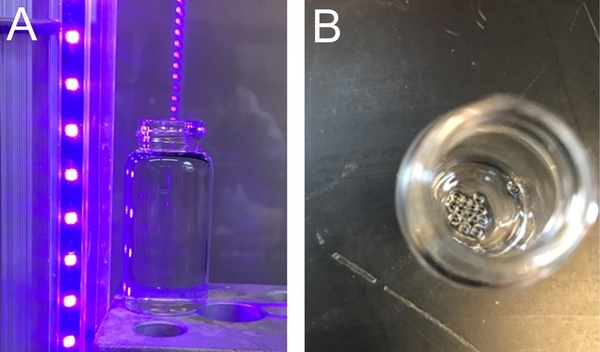
Superabsorbent beads are remarkable, used throughout our daily lives for various practical applications. These beads, as suggested by their name, possess a unique ability to absorb and retain large quantities of liquids. This characteristic of absorbency makes them essential throughout the medical field, agriculture, and other critical industries as well as in everyday products. To create these beads, the process of photopolymerization is fast growing in favor with distinct advantages of cost efficiency, speed, energy efficiency, and mindfulness towards the environment. In this article, researchers explore the pairing of cheap monomers with accessible equipment for creation of superabsorbent beads via the photopolymerization process. This research substantially demonstrates the successful application of photopolymerization in producing highly absorbent beads in a low-cost context, thereby expanding the accessibility of this process for creating superabsorbent beads in both research and practical applications.
Read More...Refinement of Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms of Atopic Dermatitis related Filaggrin through R packages

In the United States, there are currently 17.8 million affected by atopic dermatitis (AD), commonly known as eczema. It is characterized by itching and skin inflammation. AD patients are at higher risk for infections, depression, cancer, and suicide. Genetics, environment, and stress are some of the causes of the disease. With the rise of personalized medicine and the acceptance of gene-editing technologies, AD-related variations need to be identified for treatment. Genome-wide association studies (GWAS) have associated the Filaggrin (FLG) gene with AD but have not identified specific problematic single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs). This research aimed to refine known SNPs of FLG for gene editing technologies to establish a causal link between specific SNPs and the diseases and to target the polymorphisms. The research utilized R and its Bioconductor packages to refine data from the National Center for Biotechnology Information's (NCBI's) Variation Viewer. The algorithm filtered the dataset by coding regions and conserved domains. The algorithm also removed synonymous variations and treated non-synonymous, frameshift, and nonsense separately. The non-synonymous variations were refined and ordered by the BLOSUM62 substitution matrix. Overall, the analysis removed 96.65% of data, which was redundant or not the focus of the research and ordered the remaining relevant data by impact. The code for the project can also be repurposed as a tool for other diseases. The research can help solve GWAS's imprecise identification challenge. This research is the first step in providing the refined databases required for gene-editing treatment.
Read More...