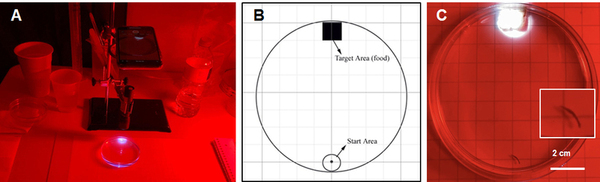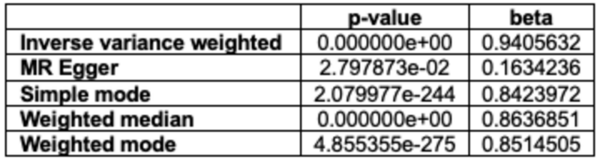
Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) and Alzheimer's Disease (AD) are distinct conditions, but research suggests a link, as individuals with ASD are 2.5 times more likely to develop AD. A study employing genome-wide association studies and Mendelian randomization revealed shared genetic factors, particularly in synaptic regulation pathways, that may increase the risk of AD in those with ASD. These findings provide insights into the genetic underpinnings connecting the two disorders.
Read More...