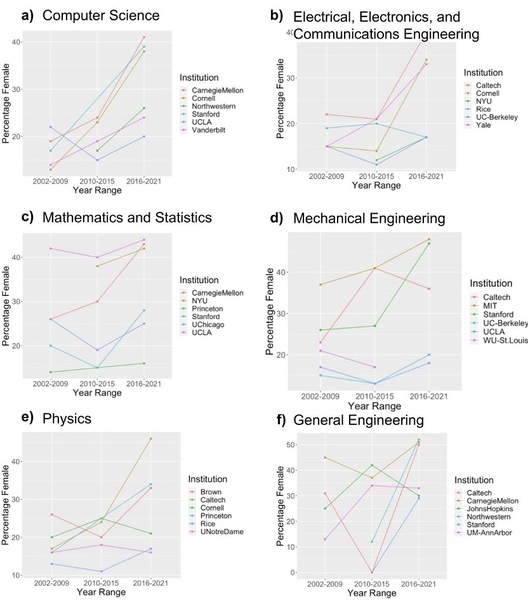
Authors address the gender disparity in STEM fields, examining changes in gender diversity across male-dominated undergraduate programs over 19 years at 24 top universities. Analyzing data from NCES IPEDS, it identifies STEM as persistently male-dominated but notes increasing gender diversity in many disciplines, particularly in recent years. Results indicate that higher-ranked universities in disciplines like computer science and mechanical engineering show a weak correlation with improved gender diversity, suggesting effective initiatives can mitigate the gender gap in STEM, despite ongoing challenges.
Read More...



.jpg)