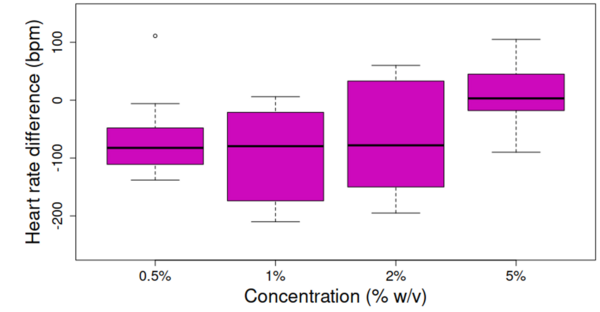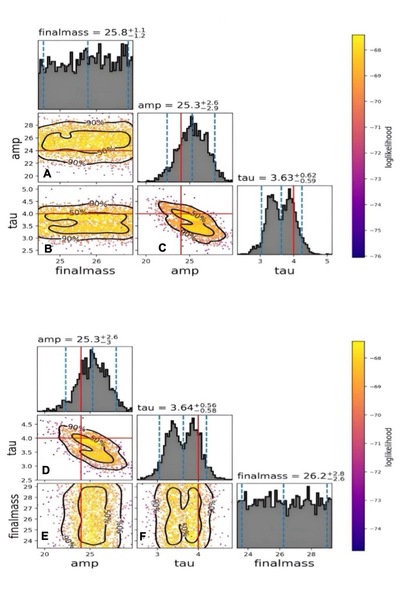
In the quest to understand dark matter, scientists face a profound mystery. Two compelling candidates, Massive Compact Halo Objects (MACHOs) and Weakly Interacting Massive Particles (WIMPs), have emerged as potential sources. By analyzing gravitational waves from binary mergers involving these black holes, authors sought to determine if MACHOs could be the elusive dark matter.
Read More...
.png)