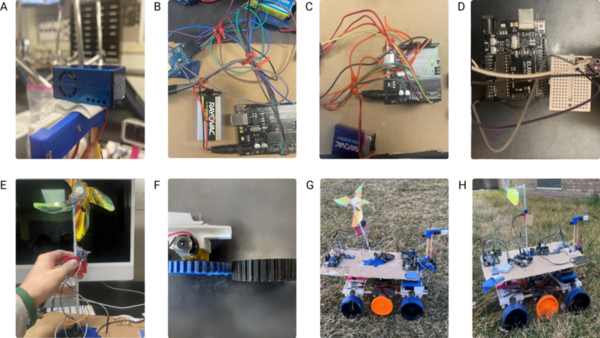
Pediatric asthma remains a significant health issue for Dallas students. This study examined the relationship between microclimatic parameters, vegetation, and pediatric asthma vulnerability (PAV) in urban schools.
Read More...Rover engineered to evaluate impacts of microclimatic parameters on pediatric asthma in Dallas schools

Pediatric asthma remains a significant health issue for Dallas students. This study examined the relationship between microclimatic parameters, vegetation, and pediatric asthma vulnerability (PAV) in urban schools.
Read More...Genetic underpinnings of the sex bias in autism spectrum disorder

Here, seeking to identify a possible explanation for the more frequent diagnosis of autism spectrum disorder (ASD) in males than females, they sought to investigate a potential sex bias in the expression of ASD-associated genes. Based on their analysis, they identified 17 ASD-associated candidate genes that showed stronger collective sex-dependent expression.
Read More...Analysis of the lung microbiome in cystic fibrosis patients using 16S sequencing
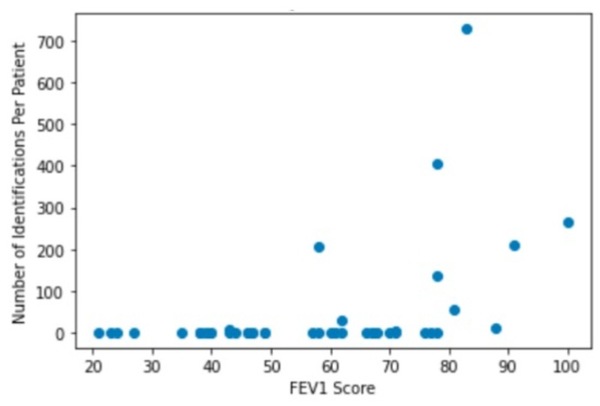
In this article the authors look at the lung microbiome in patients with cystic fibrosis to determine what the major bacterial species present are.
Read More...Characterizing Quorum Sensing-Induced Bioluminescence in Variable Volumes With Vibrio fischeri Using Computer Processing Methods
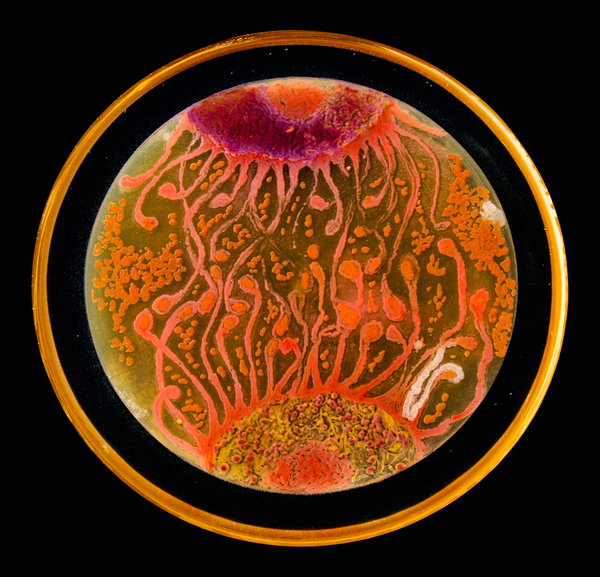
Understanding how bacteria respond to other bacteria could facilitate their ability to initiate and maintain their infectiousness. The phenomenon by which bacteria signal to each other via chemical signals is called quorum sensing, which could be targeted to deter bacterial infection in some cases if better understood. In this article, the authors study how a bacterium called V. fischeri uses quorum sensing to change bioluminescence, an easy readout that facilitates studying quorum sensing in this strain.
Read More...Effect of heme vs. non-heme iron supplements on gut microbiome fitness

Here, based on identification of iron deficiencies of a majority of people around the world, the authors sought to understand how the two main forms of dietary iron, heme and non-heme, affect the bacteria found in the human gut. by using a cell plate study, they found that bacterial growth increased with increasing concentration os either form of iron, up until the point where the high iron content resulted in cytotoxicity. They suggest this evidence points to the potential dangers of overconsumption of iron.
Read More...Determining the best convolutional neural network for identifying tuberculosis and pneumonia in chest x-rays
.png)
To best identify tuberculosis and pneumonia diagnoses in chest x-rays, the authors compare different deep learning convolution neural networks.
Read More...TNF signaling pathway upregulation as a potential pharmaceutical target for cocaine-addicted individuals

In this article, the authors investigate the RNA expression differences between groups of chronic cocaine abusers and drug-free subjects.
Read More...FCRL3 Gene Association with Asthma and Allergic Rhinitis

This study sought to determine if there is an association between the single nucleotide polymorphism rs7528684 of the Fc receptor-like-3 (FCRL3) gene and asthma or allergic rhinitis (AR). Based on previous studies in an Asian population, we hypothesized that participants with an AA genotype of FCRL3 would be more likely to have asthma and/or allergic rhinitis. To test the hypothesis, surveys were administered to participants, and genotyping was performed on spit samples via PCR, restriction digest, and gel electrophoresis.
Read More...Diagnosing hypertrophic cardiomyopathy using machine learning models on CMRs and EKGs of the heart
Here seeking to develop a method to diagnose, hypertrophic cardiomyopathy which can cause sudden cardiac death, the authors investigated the use of a convolutional neural network (CNN) and long short-term memory (LSTM) models to classify cardiac magnetic resonance and heart electrocardiogram scans. They found that the CNN model had a higher accuracy and precision and better other qualities, suggesting that machine learning models could be valuable tools to assist physicians in the diagnosis of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy.
Read More...Bacteria and Antibiotic Resistance in School Bathrooms

Since school bathrooms are widely suspected to be unsanitary, we wanted to compare the total amount of bacteria with the amount of bacteria that had ampicillin or streptomycin resistance across different school bathrooms in the Boston area. We hypothesized that because people interact with the faucet, outdoor handle, and indoor handle of the bathroom, based on whether or not they have washed their hands, there would be differences in the quantity of the bacteria presented on these surfaces. Therefore, we predicted certain surfaces of the bathroom would be less sanitary than others.
Read More...