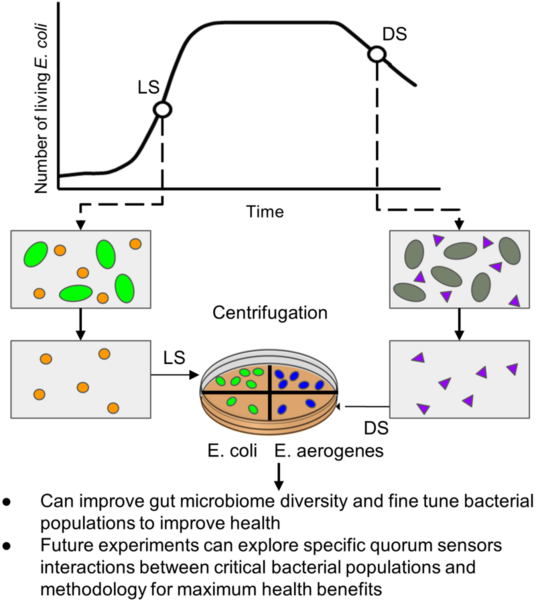
The study discusses the relationship between bacterial species and the human gut microbiome, emphasizing the role of quorum sensing molecules in bacterial communication and its implications for health. Authors investigated the impact of bacterial supernatants from Escherichia coli (E. coli) on the growth of new E. coli and Enterobacter aerogenes (E. aerogenes) cultures.
Read More...