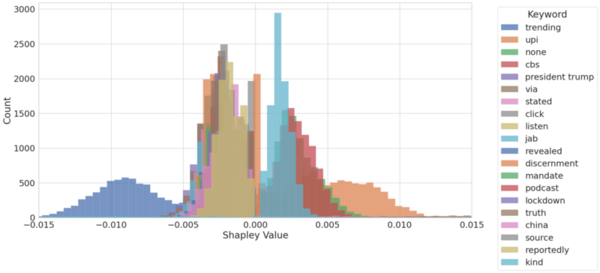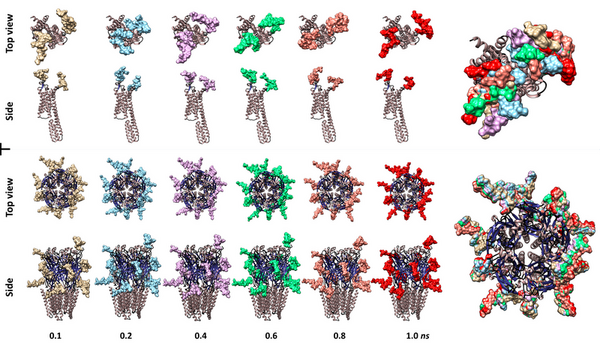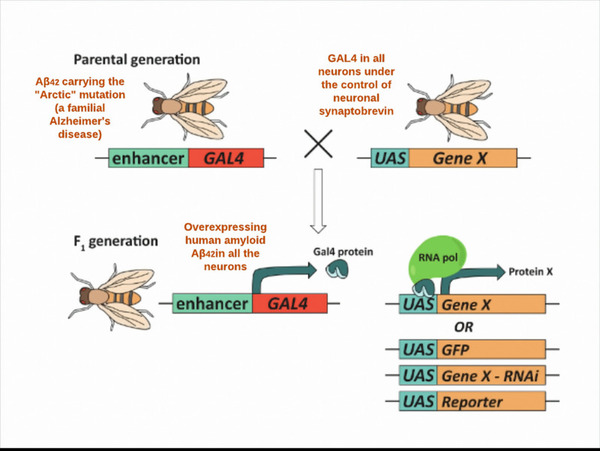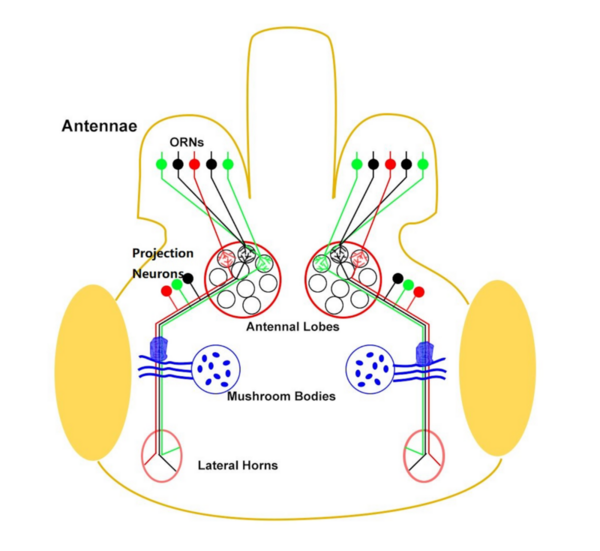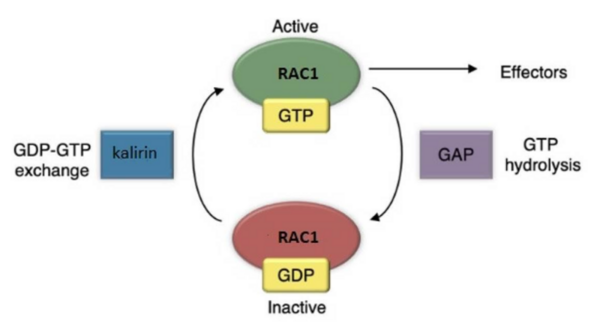
Kalirin is a guanine nucleotide exchange factor (GEF) for the GTPase RAC1, linked to schizophrenia and Alzheimer’s Disease. It plays a crucial role in synaptic plasticity by regulating dendritic spine formation and actin cytoskeleton remodeling, which are essential for creating new synapses. Authors developed two novel compounds targeting kalirin, confirming that predictive modeling can indicate biological activity.
Read More...