In this study, the authors investigate whether Moringa Oleifera seeds can serve as material to aid in purifying water. M. oleifera seeds have coagulating properties and the authors hypothesized that including it in a water filtration system would reduce particles, specifically bacteria, in water. Their results show that this system removed the largest percent of bacteria. When used in combination with cilantro, it was actually more efficient than the other techniques! These findings have important implications for creating better and more economical water purification systems.
Read More...Browse Articles
Investigating sustainable insulation materials: Analysis of biofoams and petroleum-derived foams
The authors looked into eco-friendly alternatives for insulating material. They ultimately found that a polyurethane derived from eggshells was an effective insulator and further research into it is warranted.
Read More...Innovative use of recycled textile fibers in building materials: A circular economy approach
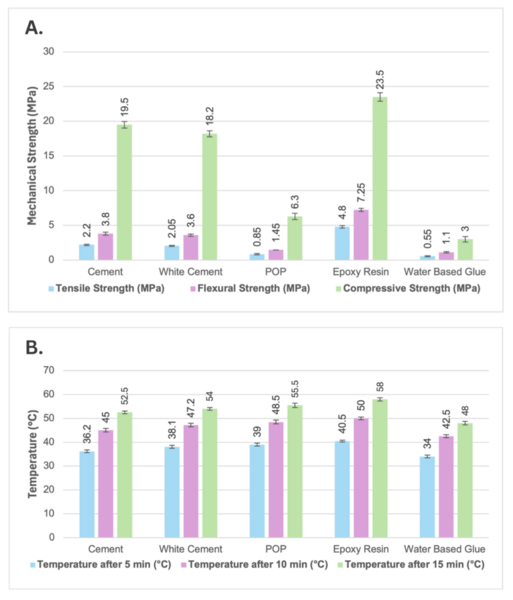
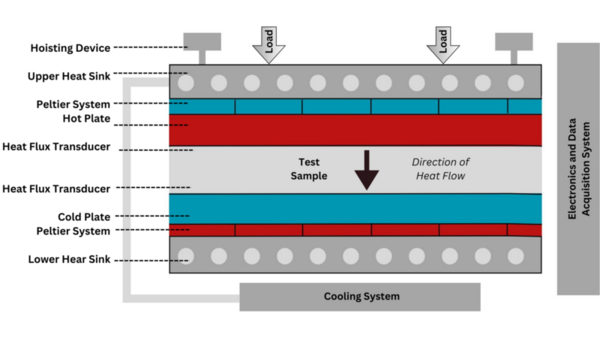
Textile waste from the fashion industry is a major environmental pollutant, but recycling waste into novel building material is a strategy to reduce the negative effects. This manuscript characterized five different binders that can be used to repurpose textile waste into bricks for construction purposes. Water-based glue, cement, white cement, plaster of Paris, and epoxy resin were mixed with shredded textile waste, and the mechanical characteristics and thermal insulation of each brick type were measured. Bricks with increased mechanical strength had the poorest thermal resistance, and the contrasting properties would suit different building purposes. This work provides a first step in generating recycled textile bricks for construction in a circular economy framework.
Read More...From trash to treasure: A sustainable approach to oil spill clean-up
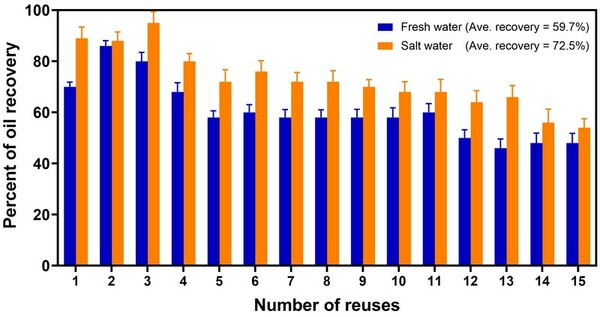
In this study the authors looked at sustainable ways to clean up oil spills that harm marine life. Using water spangle leaves and milk week the authors looked at the ability to recovery oil from both fresh and salt water and the ability to reuse the organic material to clean up spills. Their results show promise to help find a sustainable, eco-friendly way to clean up oil spills and protect marine life and habitats.
Read More...Harvesting Atmospheric Water
The objective of this project was to test various materials to determine which ones collect the most atmospheric water when exposed to the same environmental factors. The experiment observed the effect of weather conditions, a material’s surface area and hydrophilicity on atmospheric water collection. The initial hypothesis was that hydrophobic materials with the greatest surface area would collect the most water. The materials were placed in the same outside location each night for twelve trials. The following day, the materials were weighed to see how much water each had collected. On average, ribbed plastic collected 10.8 mL of water per trial, which was over 20% more than any other material. This result partially supported the hypothesis because although hydrophobic materials collected more water, surface area did not have a significant effect on water collection.
Read More...A Taste of Sweetness in Bioplastics

Sweet potatoes are one of the most common starches in Taiwan, and sweet potato peels hold significant potential to make biodegradable plastics which can alleviate the environmental impact of conventional petroleum-based plastics. In this paper, Tsai et al created starch-based bioplastics derived from sweet potato peels and manipulated the amount of added glycerol to alter the plastic’s strength and flexibility properties. Their results indicated that higher concentrations of glycerol yield more malleable plastics, providing insights into how recycled agricultural waste material might be used to slow down the rate of pollution caused by widespread production of conventional plastics.
Read More...Purification of Water by Aloe
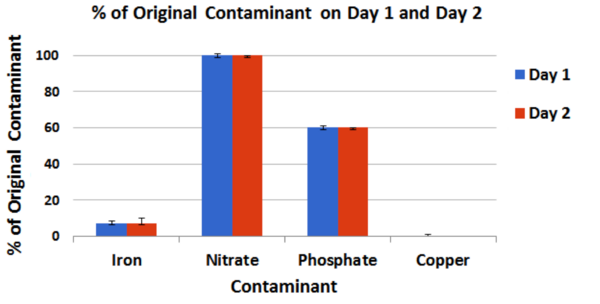
The authors test the ability of aloe vera gel to purify water of four separate contaminants. Aloe reduced the levels of copper, iron, and phosphate, but not nitrate. Potential applications of this purification system are discussed.
Read More...A systematic study of cut-resistant socks for hockey players
Enhanced soil fertility through seaweed-derived biochar: A comparative analysis with commercial fertilizers
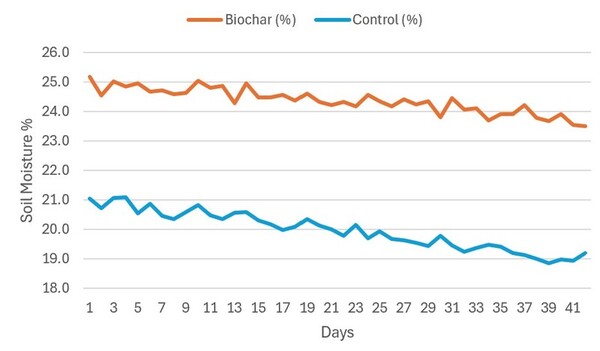
The study explored converting Gracilaria seaweed waste—known for releasing toxic hydrogen sulfide when decomposed—into biochar as a sustainable solution for waste management and soil improvement.
Read More...Testing filtration capabilities of household fabrics for protection against airborne contaminants
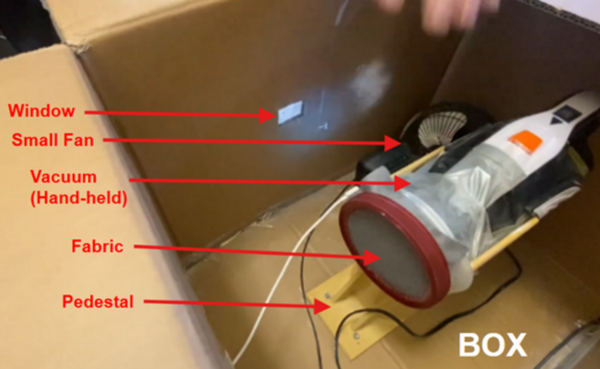
Toxic particulates in the atmosphere pose significant health risks, and while modern masks can help reduce inhalation of these pollutants, their availability may be limited during health crises. This study evaluated the effectiveness of household fabrics (cotton, fleece, wool, and rayon) as particulate filters, finding that cotton outperformed the others in filtration efficiency, while rayon was the least effective. The findings suggest that cotton is a preferable alternative for filtration purposes, while rayon should be avoided.
Read More...