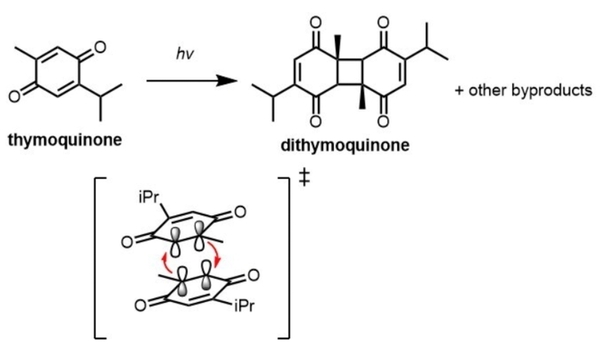
Berberine, a natural product alkaloid, has been shown to exert biological activity via in situ production of singlet oxygen when photo irradiated. Berberine utilizes singlet oxygen in its putative mechanism of action, wherein it forms an activated complex with DNA and photosensitizes triplet oxygen to singlet oxygen to specifically oxidize guanine residues, thereby halting cell replication and leading to cell death. This has potential application in photodynamic therapy, alongside other such compounds which also act as photosensitizers and produce singlet oxygen in situ. The quantification of singlet oxygen in various photosensitizers, including berberine, is essential for determining their photosensitizer efficiencies. We postulated that the singlet oxygen produced by photoirradiation of berberine would be superior in terms of singlet oxygen production to the aforementioned photosensitizers when irradiated with UV light, but inferior under visible light conditions, due to its strong absorbance of UV wavelengths.
Read More...