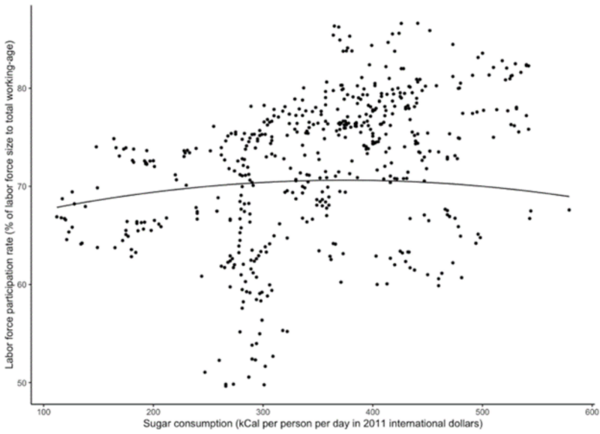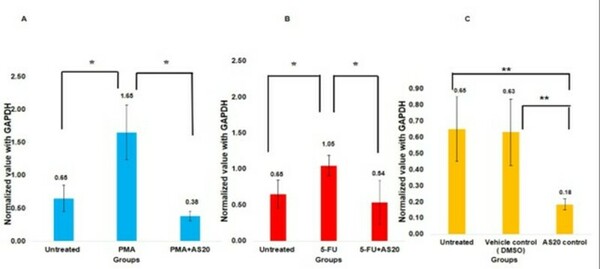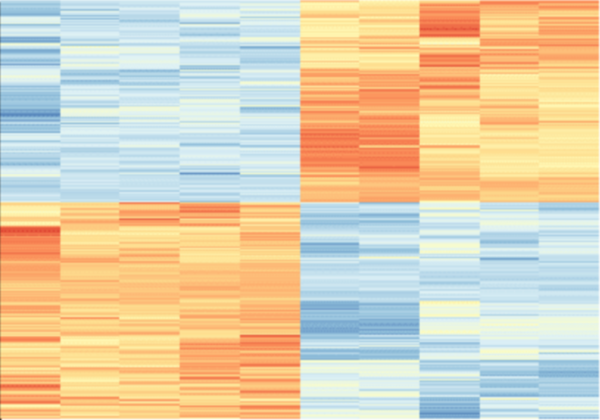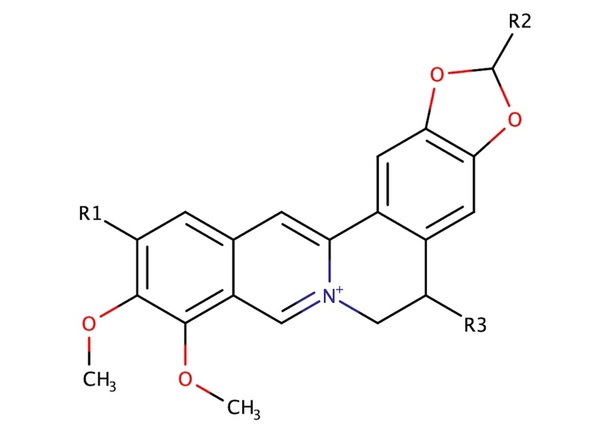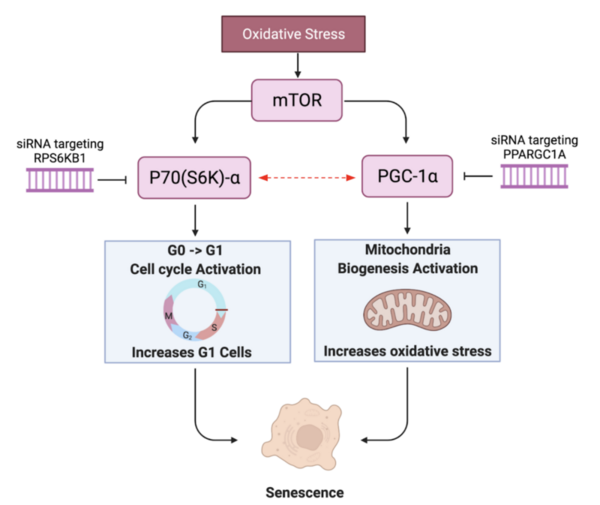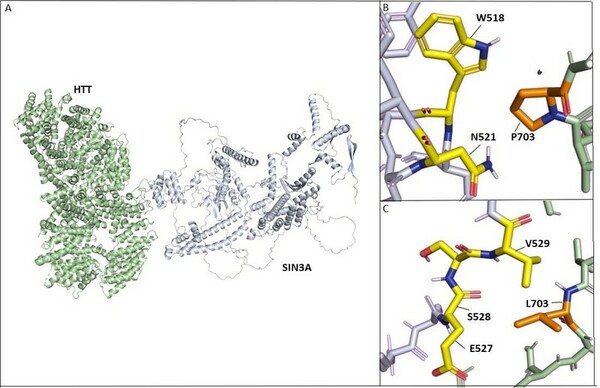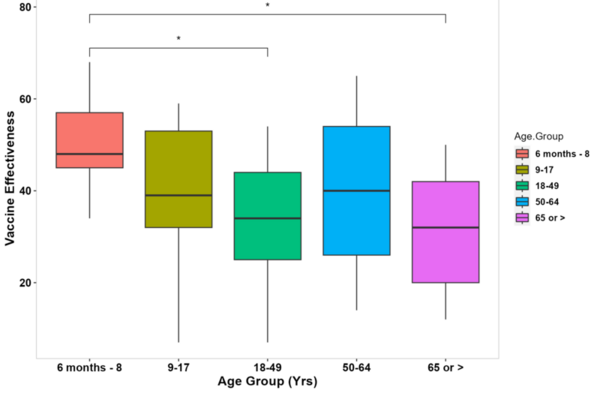
In this manuscript the authors looked at current vaccine strategies against different strains of influenza. Looking at several factors they found that influenza strain as well as vaccinated age group, among other factors, impact vaccine effectiveness.
Read More...