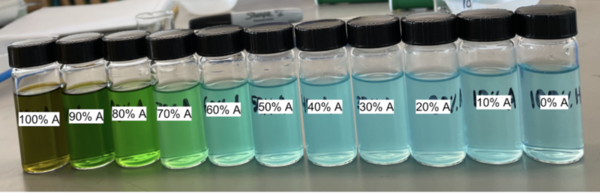
In this study, the authors investigate the effects of acetone on the color of copper chloride (CuCl2) solution, which has important implications for detecting copper in the environment.
Read More...A colorimetric investigation of copper(II) solutions

In this study, the authors investigate the effects of acetone on the color of copper chloride (CuCl2) solution, which has important implications for detecting copper in the environment.
Read More...A Phylogenetic Study of Conifers Describes Their Evolutionary Relationships and Reveals Potential Explanations for Current Distribution Patterns
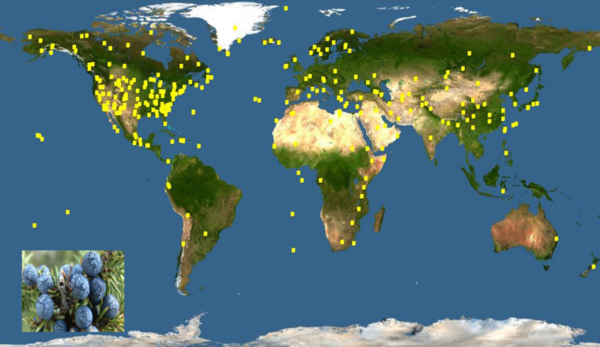
Many species of trees are distributed widely around the world, though not always in a way that makes immediate sense. The authors here use genetic information to help explain the geographic distribution of various conifer species throughout the world.
Read More...The Effect of Font Type on a School’s Ink Cost

Your choice of font can impact more than style. Here the authors demonstrate that font choice can affect the amount of ink a given print-out requires. The authors estimate that a switch to Garamond font, size 12, by all teachers in his school district would save almost $21,000 annually.
Read More...Evaluating the antimicrobial activity of maitake mushroom extract against Staphylococcus epidermidis
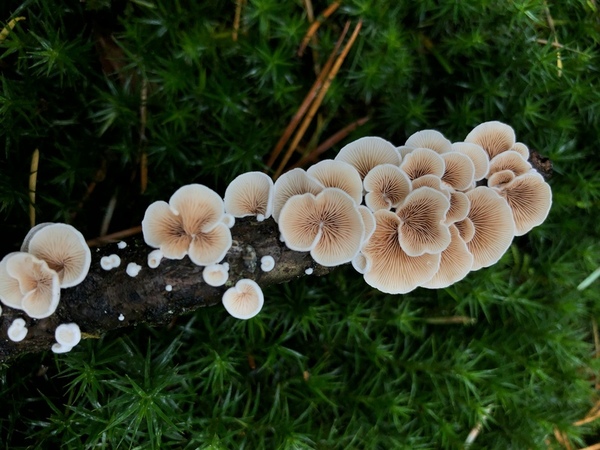

Here, seeking to explore new antimicrobial therapies, the authors investigated the antimicrobial activity of Maitake mushroom extract against Staphylococcus epidermidis, a common cause of antibiotic resistant hospital-acquired infections. They found that Maitake extract showed potent antimicrobial activity, with higher concentrations showing inhibition comparable to tetracycline.
Read More...A chemical and overwintering honey bee apiary field study comparing new and expired amitraz miticide

In this study, the authors test the longevity of a anti-mite compound, amitraz, in commercially-sold strips and the age-dependent efficacy of these strips in preventing honey bee colony collapse by ectoparasitic mite Varroa destructor.
Read More...Copper nanoparticle synthesis using Picea glauca ‘Conica’
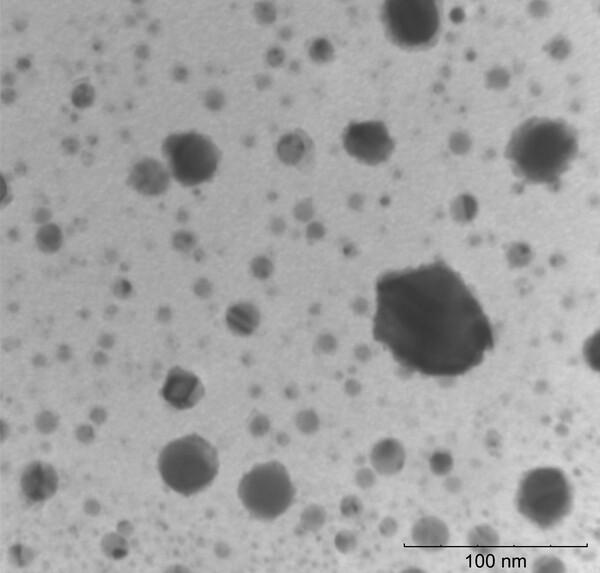
The authors propose a method to recycle Christmas tree needles into a non-toxic reducing agent for synthesizing copper nanoparticles.
Read More...Earthworms as soil quality indicators: A case study of Crissy Field and Bayview Hunters Point naval shipyard

The authors looked at soil quality of former military sites where chemical disposal was known to have occurred. Along with testing for heavy metals, the authors also looked for the presence (and number) of earthworms present in topsoil samples as a marker of soil health.
Read More...Utilizing sorbitol to improve properties of cellulose-based biodegradable hydrogels
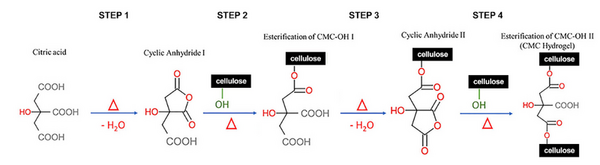
Hydrogels are commonly used in medicine, pharmaceuticals, and agriculture. Hydrogels absorb water by swelling and re-release this water by diffusion. This study sought to synthesize a biodegradable, cellulose-based hydrogel that is more effective at absorbing and re-releasing water than those produced by current methods. We tested the compressive strength of both the dry and swollen gels and the tensile strength of the swollen gels to elucidate the gel structure.
Read More...Efficacy of natural coagulants in reducing water turbidity under future climate change scenarios

Here the authors investigated the effects of natural coagulants on reducing the turbidity of water samples from the Tennessee River Watershed. They found that turbidity reduction was higher at lower temperatures for eggshells. They then projected and mapped turbidity reactions under two climate change scenarios and three future time spans for eggshells. They found site-specific and time-vary turbidity reactions using natural coagulants could be useful for optimal water treatment plans.
Read More...Assessing the association between developed surface area and land surface temperature of urban areas
Almost all urban areas face the challenge of urban heat islands, areas with substantially hotter land surface temperatures than the surrounding rural areas. These areas are associated with worse air and water
quality, increased power outages, and increased heat-related illnesses. To learn more about these areas, Ustin et al. analyze satellite images of Cleveland neighborhoods to find out if there is a correlation between surface area development and surface temperature.