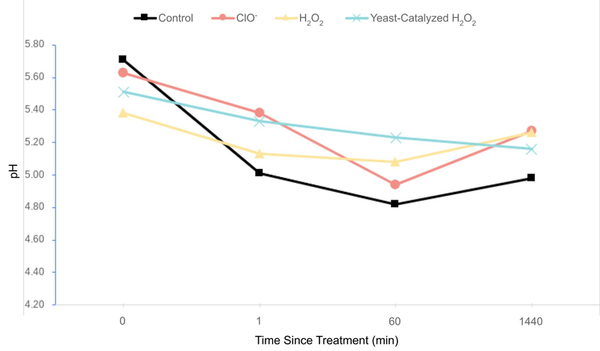
The authors looked at different treatments to clean up rainwater collected at home. They found that chlorine treatment and treatment with hydrogen peroxide catalyzed by yeast showed similar potential for cleaning up contaminated rainwater, but that further studies are needed to better assess impact on specific contaminant levels still present.
Read More...