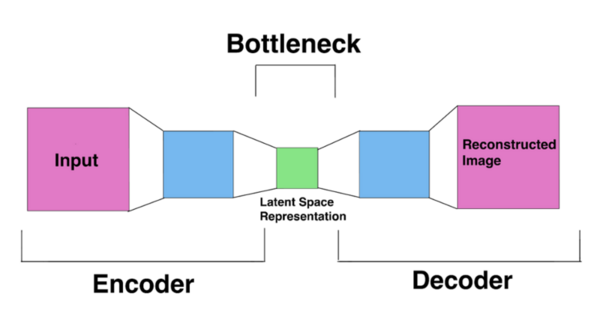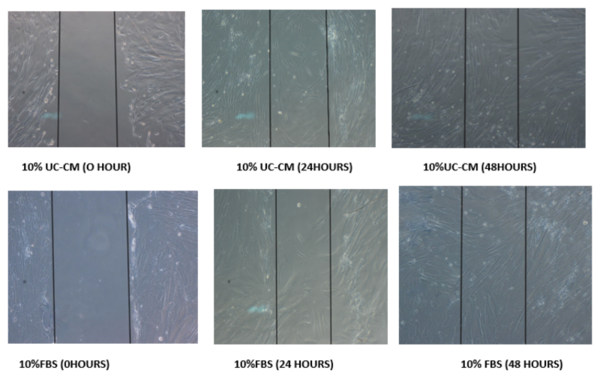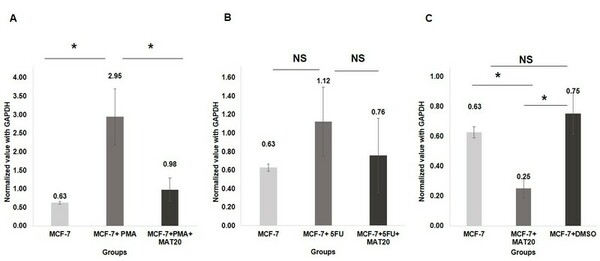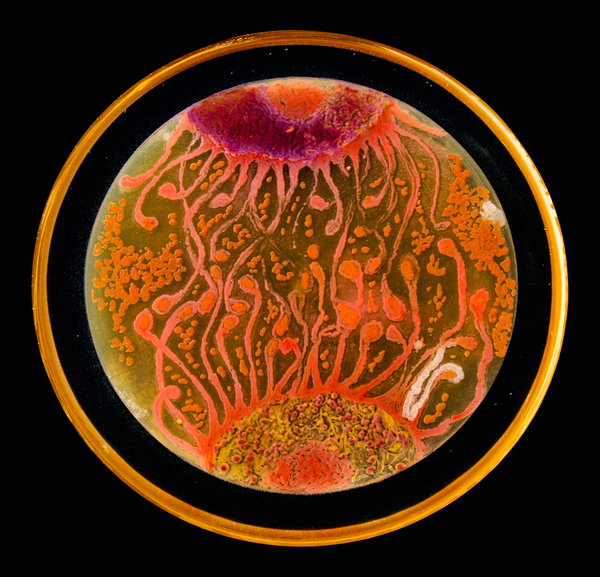
Understanding how bacteria respond to other bacteria could facilitate their ability to initiate and maintain their infectiousness. The phenomenon by which bacteria signal to each other via chemical signals is called quorum sensing, which could be targeted to deter bacterial infection in some cases if better understood. In this article, the authors study how a bacterium called V. fischeri uses quorum sensing to change bioluminescence, an easy readout that facilitates studying quorum sensing in this strain.
Read More...