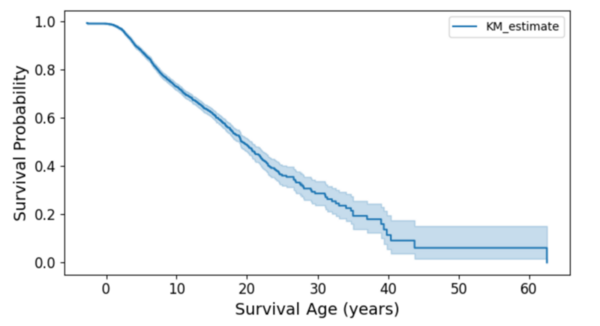
Pediatric cancers pose unique challenges due to their rarity and distinct biological factors, emphasizing the need for accurate survival prediction to guide treatment. This study integrated generative AI and machine learning, including synthetic data, to analyze 9,184 pediatric cancer patients, identifying age at diagnosis, cancer types, and anatomical sites as significant survival predictors. The findings highlight the potential of AI-driven approaches to improve survival prediction and inform personalized treatment strategies, with broader implications for innovative healthcare applications.
Read More...