Advancing pediatric cancer predictions through generative artificial intelligence and machine learning
(1) Vista Ridge High School, (2) QuantaHealth Research Institute
https://doi.org/10.59720/24-175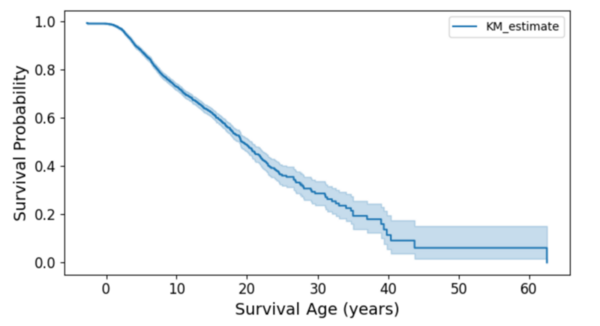
Pediatric cancers present unique challenges due to their rarity and the distinct biological factors involved, making early and accurate prediction of survival outcomes critical for guiding treatment. Recent advancements in artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) have shown promise in enhancing predictive models for various diseases, including cancer. This study aimed to identify key factors influencing survival rates in pediatric cancer patients through the integration of generative AI and machine learning techniques, including the use of synthetic data. We hypothesized that age at diagnosis was an important predictor of survival outcomes, alongside other significant demographic and clinical variables. Our hypothesis is supported by our analysis, which includes 9184 pediatric cancer patients. Our results indicate that age at diagnosis, specific cancer types, and anatomical sites are significant predictors of survival. Stratification analyses and Kaplan-Meier survival curves consistently show that earlier diagnosis is associated with better survival outcomes, particularly for diagnoses such as neuroblastoma, B lymphoblastic leukemia/lymphoma with hyper diploidy, and osteosarcoma. Comparative analysis and sensitivity tests confirmed age at diagnosis as a critical factor. Classification models enhanced with synthetic data achieved an overall accuracy of 0.74, reflecting the potential of integrating AI-driven approaches with real and synthetic data to improve survival prediction. Broader impacts of this study include its potential to influence pediatric cancer treatment protocols by identifying high-risk groups early, thereby improving personalized treatment strategies. Additionally, this research demonstrates the utility of AI and synthetic data in healthcare, paving the way for more innovative applications across different medical fields.
This article has been tagged with: