%20(1).png)
In this study, the authors identify transcripts and gene networks that are changed after infection with the Middle East Respiratory Syndrome-related coronavirus (MERS-CoV).
Read More...Gene expression profiling of MERS-CoV-London strain
%20(1).png)
In this study, the authors identify transcripts and gene networks that are changed after infection with the Middle East Respiratory Syndrome-related coronavirus (MERS-CoV).
Read More...Effects of Photoperiod Alterations on Stress Response in Daphnia magna
Here, seeking to better understand the effects of altered day-night cycles, the authors considered the effects of an altered photoperiod on Daphnia magna. By tracking possible stress responses, including mean heart rate, brood size, and male-to-female ratio they found that a shorter photoperiod resulted in altered mean heart rates and brood size. The authors suggest that based on these observations, it is important to consider the effects of photoperiod alterations and the stress responses of other organisms.
Read More...Do trumpet players have a greater expiratory capacity than those who do not play a wind instrument?

With healthy lung performance being critical to daily function and maintenance of physical health, the authors of this study explored the impact of airflow training from playing a wind instrument on respiratory system function. With careful quantification of peak expiratory flow of individuals who played the trumpet, the authors found no expiratory capacity difference between students who played the trumpet and students who did not play a wind instrument.
Read More...The knowledge and perception of opioid abuse and its long-term effects among high schoolers
Due to the susceptibility of adolescent age groups to opioid misuse, here the authors sought to determine if there was a difference in the perception and knowledge between 9th and 12th graders regarding the opioid crisis. An educational intervention trial was done with the 9th graders and surveys were used to identify its effects. Although the authors acknowledge a small sample size, their results suggest that their are gaps within the knowledge of adolescents in regards to opioid misuse and its long-term effects that could be addressed with further education.
Read More...COVID-19 and air pollution in New York City

Did the COVID-19 pandemic and travel restrictions improve air quality? The authors investigate this question in New York City using existing pollution data and forecasting trends.
Read More...A bibliometric analysis of the use of biomimetic silk conduits for treating peripheral nerve injuries
In this study, the authors conduct a bibliometric analysis to understand the recent growth in and current state of peripheral nerve regeneration research. They also explored potential future studies.
Read More...Presence of Vegetation in Relation to Slope in Yosemite Valley, California
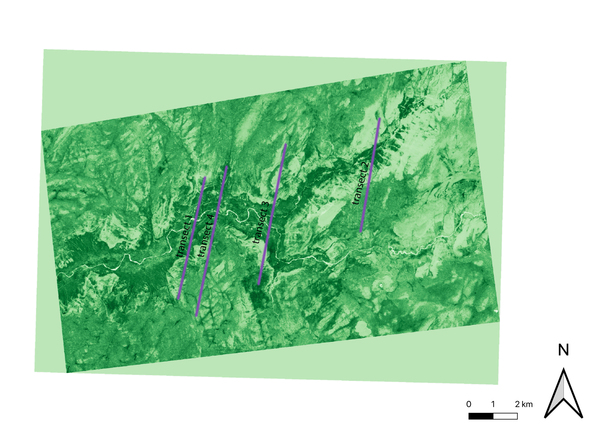
This study examined the relationship between the slope of a terrain and vegetation, measured by the normalized difference vegetation index (NDVI). It was hypothesized that lower slope ranges would be more supportive of vegetation growth than higher slope ranges. Analysis showed that no slope (even as extreme as 85–90°) prohibits the growth of vegetation completely; even the steepest slopes examined contain plant life. Knowing that steep slopes can still support plant life, agriculturalists can begin to explore and start planting additional crops and plants at these extreme slopes.
Read More...Testing HCN1 channel dysregulation in the prefrontal cortex using a novel piezoelectric silk neuromodulator
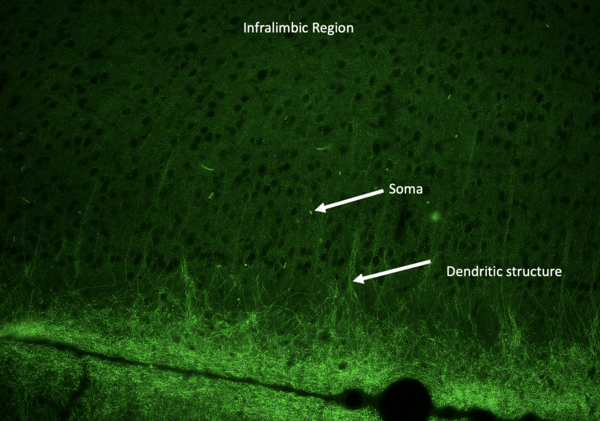
Although no comprehensive characterization of schizophrenia exists, there is a general consensus that patients have electrical dysfunction in the prefrontal cortex. The authors designed a novel piezoelectric silk-based implant and optimized electrical output through the addition of conductive materials zinc oxide (ZnO) and aluminum nitride (AlN). With further research and compatibility studies, this implant could rectify electrical misfiring in the infralimbic prefrontal cortex.
Read More...Exploring Unconventional Growing Methods to Promote Healthy Growth in Common Household Plants: Tagetes patula L. and Lepidium sativum

This study focused on finding more sustainable growing methods that reduce chemical fertilizer or water usage and can be used at the household level for garden plants. Metrics for healthy plant growth were height at first bloom, growing time, and survival rate. The Deep Water Culture (DWC) treatment for garden cress plants significantly increased the height at first bloom compared to the control group. For rates of surviving plants, the treatments had little effect on garden cress, but the Eggshell Grounds, Wick System, and DWC system groups outperformed the control group for marigolds.
Read More...Discovery of the Heart in Mathematics: Modeling the Chaotic Behaviors of Quantized Periods in the Mandelbrot Set
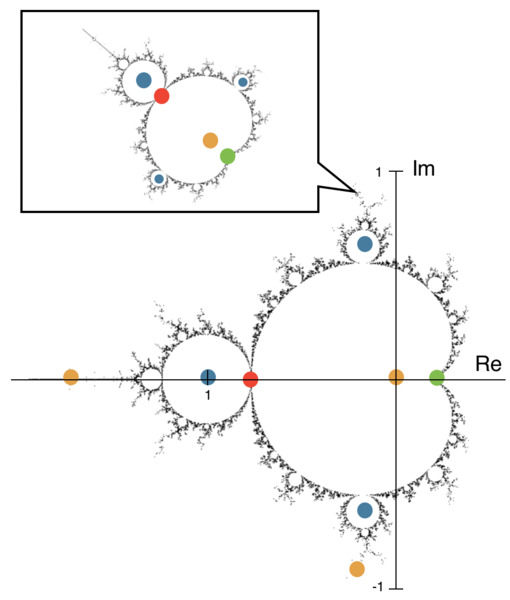
This study aimed to predict and explain chaotic behavior in the Mandelbrot Set, one of the world’s most popular models of fractals and exhibitors of Chaos Theory. The authors hypothesized that repeatedly iterating the Mandelbrot Set’s characteristic function would give rise to a more intricate layout of the fractal and elliptical models that predict and highlight “hotspots” of chaos through their overlaps. The positive and negative results from this study may provide a new perspective on fractals and their chaotic nature, helping to solve problems involving chaotic phenomena.
Read More...