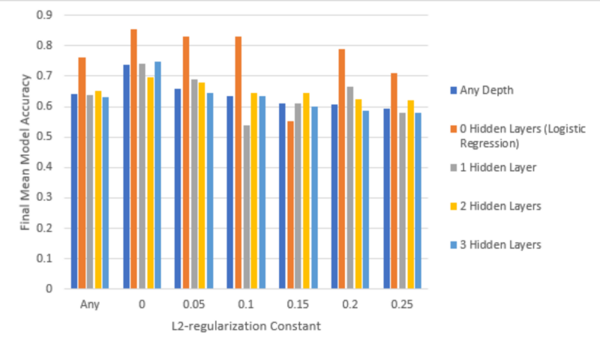
The authors looked at the ability to detect heart disease before the onset of severe clinical symptoms.
Read More...Study of neural network parameters in detecting heart disease

The authors looked at the ability to detect heart disease before the onset of severe clinical symptoms.
Read More...Using broad health-related survey questions to predict the presence of coronary heart disease
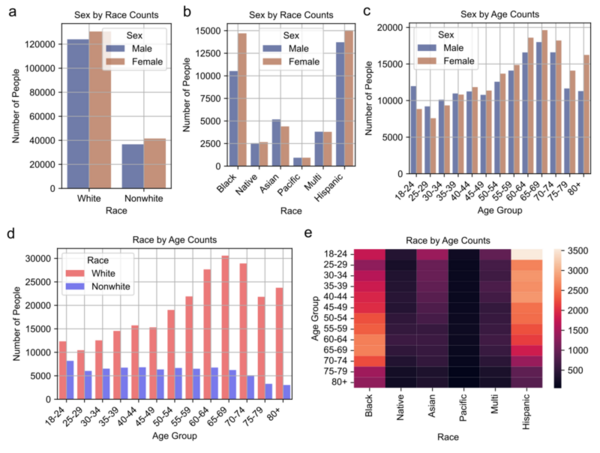
Coronary heart disease (CHD) is the leading cause of death in the U.S., responsible for nearly 700,000 deaths in 2021, and is marked by artery clogging that can lead to heart attacks. Traditional prediction methods require expensive clinical tests, but a new study explores using machine learning on demographic, clinical, and behavioral survey data to predict CHD.
Read More...Misconceptions regarding heart disease are prevalent among american adults and minors
In this study, the authors created a survey to assess misconceptions and knowledge deficits regarding cardiovascular diseases exist among US adults and minors.
Read More...Survival analysis in cardiovascular epidemiology: nexus between heart disease and mortality
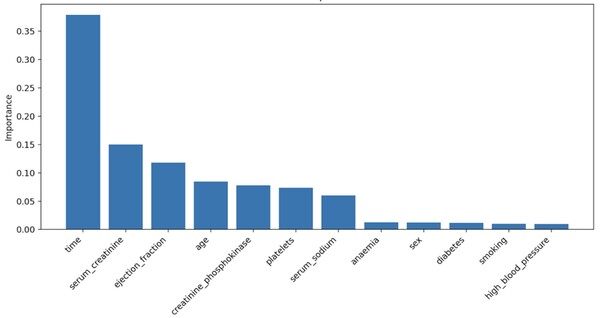
In 2021, over 20 million people died from cardiovascular diseases, highlighting the need for a deeper understanding of factors influencing heart failure outcomes. This study examined multiple variables affecting mortality after heart failure, using random forest models to identify time, serum creatinine, and ejection fraction as key predictors. These findings could contribute to personalized medicine, improving survival rates by tailoring treatment strategies for heart failure patients.
Read More...Deciphering correlation and causation in risk factors for heart disease with Mendelian randomization

Here, seeking to identify the risk of coronary artery disease (CAD), a major cause of cardiovascular disease, the authors used Mendelian randomization. With this method they identified several traits such as blood pressure readings, LDL cholesterol and BMI as significant risk factors. While other traits were not found to be significant risk factors.
Read More...Comparing the Effect of Stent Geometry on Blood Flow Rate of Curved Coronary Artery Stenosis
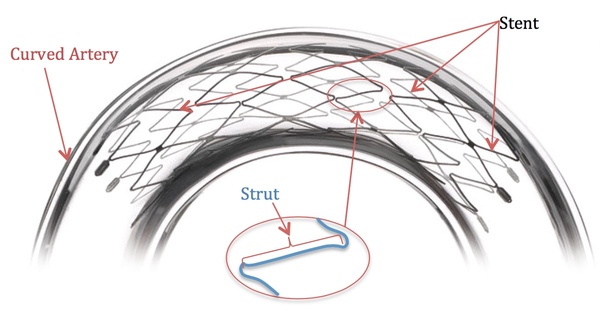
Coronary heart disease (CHD) is a global disease that causes fatal buildup of plaque in the arteries. Currently stents are placed in the artery for many patients with CHD to support proper blood flow. Here, the authors build a system to explore how the shape of the stent affects blood flow rate, a finding that can help optimize stents for patients.
Read More...Cardiovascular Disease Prediction Using Supervised Ensemble Machine Learning and Shapley Values
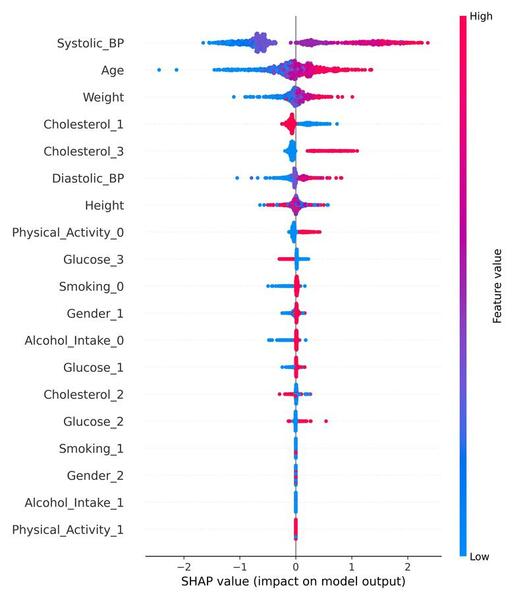
The authors test the effectiveness of machine learning to predict onset of cardiovascular disease.
Read More...A Novel Method for Auto-Suturing in Laparoscopic Robotic-Assisted Coronary Artery Bypass Graft (CABG) Anastomosis
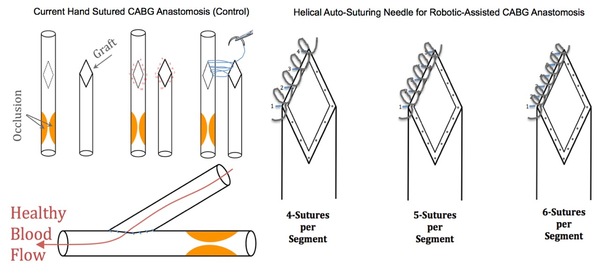
Levy & Levy tackle the optimization of the coronary artery bypass graft, a life-saving surgical technique that treats artery blockage due to coronary heart disease. The authors develop a novel auto-suturing method that saves time, allows for an increased number of sutures, and improves graft quality over hand suturing. The authors also show that increasing the number of sutures from four to five with their new method significantly improves graft quality. These promising findings may help improve outcomes for patients undergoing surgery to treat coronary heart disease.
Read More...Comparing Suturing And Stapling In Coronary Bypass Grafting Anastomosis
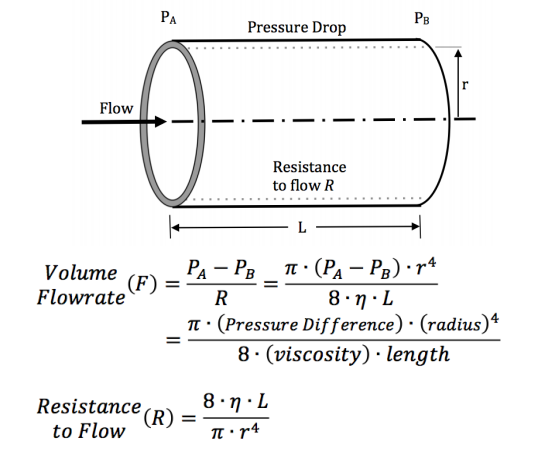
Coronary artery bypass grafts are a common technique to treat coronary heart disease. The authors compared the efficacy of suturing and stapling techniques using an artificial heart pump and silicone tubing and found that suturing, while more time and skill intensive, held pressure in the tubing better than stapling.
Read More...Examining the prevalence of depression in coronary artery disease patients: a cross-sectional analysis
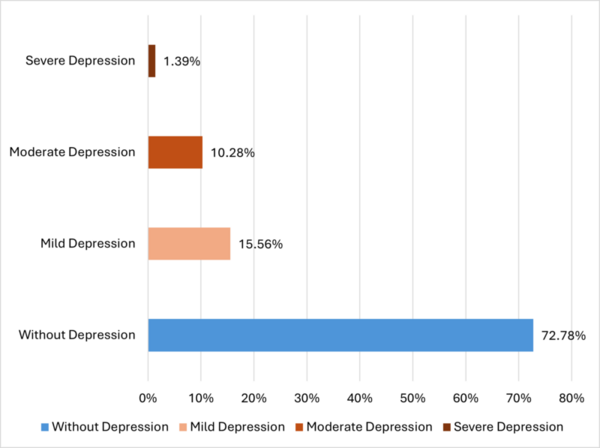
The authors surveyed individuals diagnosed with coronary artery disease about their mental health to study a potential connection between coronary artery disease and depression.
Read More...