Study of neural network parameters in detecting heart disease
(1) Newton North High School
https://doi.org/10.59720/24-281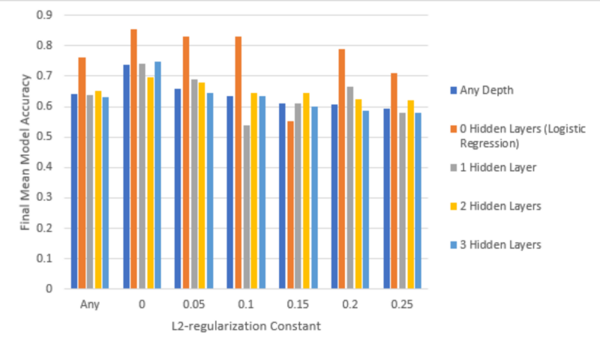
Heart disease is a major health problem worldwide, and in the United States it causes over half a million deaths per year. Machine learning algorithms are being used more widely in medicine, leading to the possibility of using machine learning to identify heart disease with greater accuracy before it presents. Machine learning would also allow for more patients to be screened, helping patients and doctors make an informed decision before any damage is done. We examined the accuracy of different machine learning models in predicting heart disease from a set of 301 patients. Specifically, we aimed to identify the optimal parameters for the accurate detection of heart disease. We hypothesized that increasing the value of the L2-regularization constant and the number of layers would increase accuracy; however, our results showed lower values of the L2-regularization constant for error regularization and lower numbers of rectified linear unit (ReLU) layers to be beneficial for the function of the model. The average accuracy after 600 epochs of models without error regularization was 73.75%, while the average final accuracy for models that utilized any non-zero value of the L2-regularization constant was consistently less than or equal to 66.02%. Of all the models studied, only two had a higher accuracy (86.64%) than a logistic regression (85.53%). As such, we found that error regularization and large models may be poorly suited for detecting heart disease, and models with one or no hidden layers may perform better than models with greater amounts of ReLU nodes. This may be significant when designing fast, accurate, and life-saving diagnostic models.
This article has been tagged with: