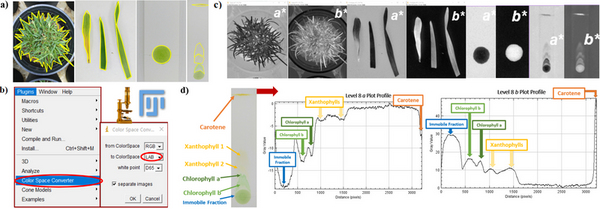
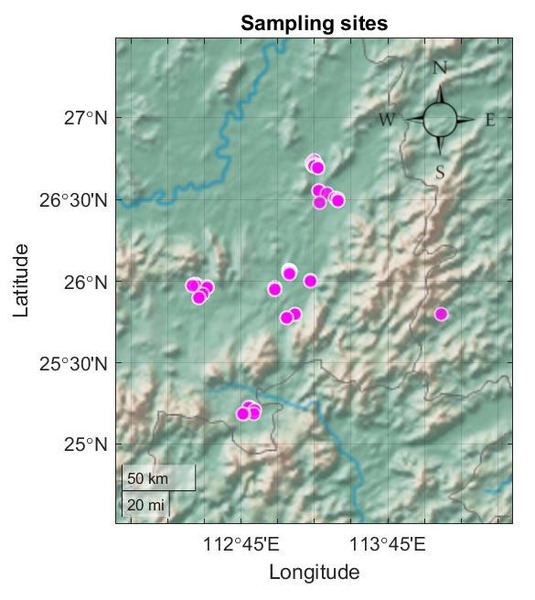
Unprocessed water from hand-pressed wells is still commonly used as a source of drinking water in Chenzhou, the “Nonferrous Metal Village” of China. Long et al. conducted a study to measure the heavy metal contamination levels and potential health effects in this area. Water samples were analyzed through Inductively Coupled Plasma Optical Emission Spectroscopy (ICPOES) and the concentrations of 20 metal elements. Results showed that although none of the samples had dangerous levels of heavy metals, the concentrations of Al, Fe, and Mn in many locations substantially exceeded those suggested in the Chinese Drinking Water Standard and the maximum contaminant levels of Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). The authors have made an important discovery regarding the water safety in HuNan and their suggestions to install water treatment systems would greatly benefit the community.
Read More...