The authors trained a machine learning model to detect kidney stones based on characteristics of urine. This method would allow for detection of kidney stones prior to the onset of noticeable symptoms by the patient.
Read More...A machine learning approach to detect renal calculi by studying the physical characteristics of urine

The authors trained a machine learning model to detect kidney stones based on characteristics of urine. This method would allow for detection of kidney stones prior to the onset of noticeable symptoms by the patient.
Read More...Paralyzing effects of CO2 and hypothermia on Madagascar hissing and dubia cockroaches

Here the authors sought to find a more ethical and efficient way to temporary paralyze a cockroach by comparing the results of two methods. By comparing immobilization through immersion in cold water and exposure to a 100 % CO2 environment, they found that cockroaches could be immobilized and recovered significantly faster when exposed to CO2.
Read More...The effects of age on quality of mental health during the COVID-19 pandemic
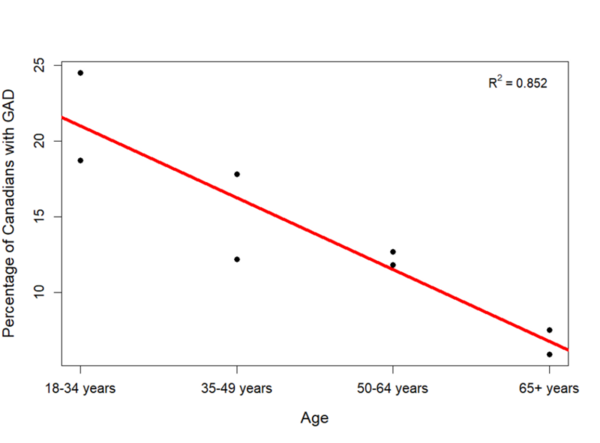
The impact of age on mental health is a crucial yet understudied aspect of public health. While mental health is gaining recognition as a vital component of overall well-being, its correlation with age remains largely unexplored. In Canada, where the median age has risen significantly over the past half-century, understanding this relationship becomes increasingly pertinent. Researchers hypothesized that older adults would exhibit lower rates of mental health disorders and report better perceived mental health due to increased emotional stability and maturity.
Read More...Differences in the effect of copper sulfate on the mortality rate of Ostracod and Daphnia
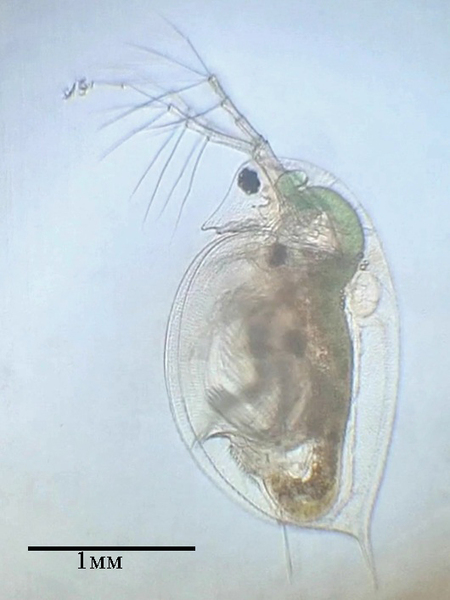
Chemical pollution can have significant effects on freshwater organisms. In this study, the effect of copper sulfate on the survival of Daphnia pulex and Ostracoda was investigated.
Read More...Effects of different synthetic training data on real test data for semantic segmentation
Semantic segmentation - labelling each pixel in an image to a specific class- models require large amounts of manually labeled and collected data to train.
Read More...Similarity Graph-Based Semi-supervised Methods for Multiclass Data Classification
The purpose of the study was to determine whether graph-based machine learning techniques, which have increased prevalence in the last few years, can accurately classify data into one of many clusters, while requiring less labeled training data and parameter tuning as opposed to traditional machine learning algorithms. The results determined that the accuracy of graph-based and traditional classification algorithms depends directly upon the number of features of each dataset, the number of classes in each dataset, and the amount of labeled training data used.
Read More...Artificial intelligence face-tracking for a semi-virtual reality gaming experience

The authors studied the impact of AI face-tracking technology on the immersiveness of videogames as an alternative to virtual reality gaming.
Read More...Effects of caffeine on muscle signals measured with sEMG signals

Here, the authors used surface electromyography to measure the effects of caffeine intake on the resting activity of muscles. They found a significant increase in the measured amplitude suggesting that caffeine intake increased the number of activated muscle fibers during rest. While previous research has focused on caffeine's effect on the contraction signals of muscles, this research suggests that its effects extend to even when a muscle is at rest.
Read More...Ladder Fuel Treatments Effect Burn Area of Forest Fires in Semi-Arid High Elevation Climates

In this study, the authors investigate a timely and important topic: forest fires. More specifically, they use a wildfire simulator to test how ladder fuels effect the burn area of a forest fire. Ladder fuels are fuels that cause a forest fire to rise up from the forest floor to the canopy, which may affect the overall spread. They simulated fire spread with different levels of ladder fuel treatment and found that the spread of a burn area would indeed decrease with increased ladder fuel treatment. These findings have important implications for forest and forest fire management.
Read More...Converting SiO2 wafers to hydrophobic using chlorotrimethylsilane
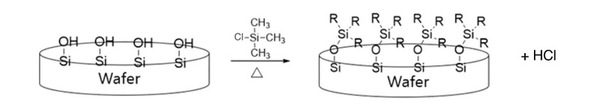
Semiconductors are the center of the fourth industrial revolution as they are key components for all electronics. Exposed wafers made of silicon (Si), which can easily oxidize, convert to silicon dioxide (SiO2). The surface of SiO2 wafers consists of many Si-OH bonds, allowing them to easily bond with water, resulting in a “wet” or hydrophilic condition. We sought to determine a way to modify the surface of SiO2 wafers to become hydrophobic to ensure safe wet cleaning.
Read More...