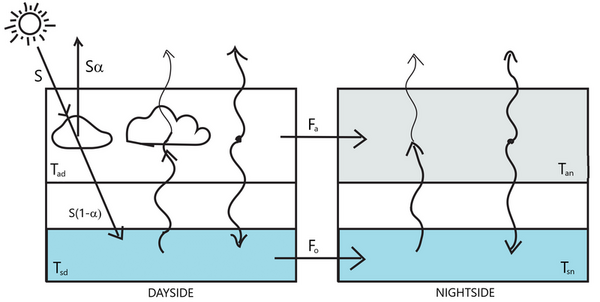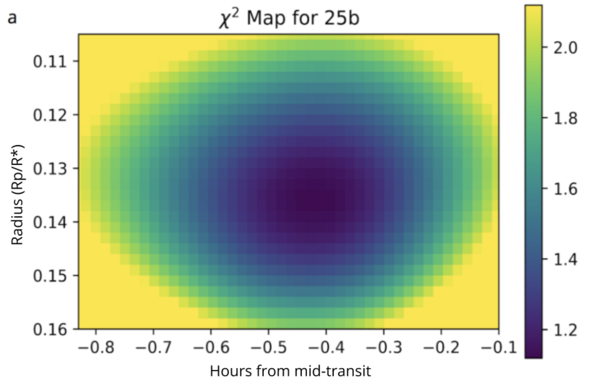
Studying exoplanets, or planets that orbit a star other than the Sun, is critical to a greater understanding the formation of planets and how Earth's solar system differs from others. In this study the authors analyze the transit light curves of three hot Jupiter exoplanets to ultimately determine if and how these planets have changed since their discovery.
Read More...