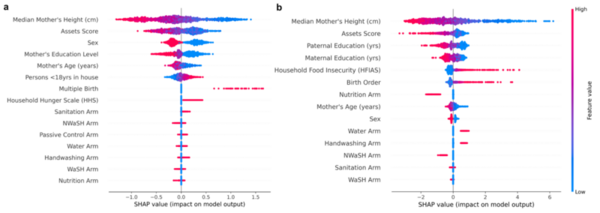
Over the last few decades, childhood stunting has persisted as a major global challenge. This study hypothesized that TPTO (Tree-based Pipeline Optimization Tool), an AutoML (automated machine learning) tool, would outperform all pre-existing machine learning models and reveal the positive impact of economic prosperity, strong familial traits, and resource attainability on reducing stunting risk. Feature correlation plots revealed that maternal height, wealth indicators, and parental education were universally important features for determining stunting outcomes approximately two years after birth. These results help inform future research by highlighting how demographic, familial, and socio-economic conditions influence stunting and providing medical professionals with a deployable risk assessment tool for predicting childhood stunting.
Read More...