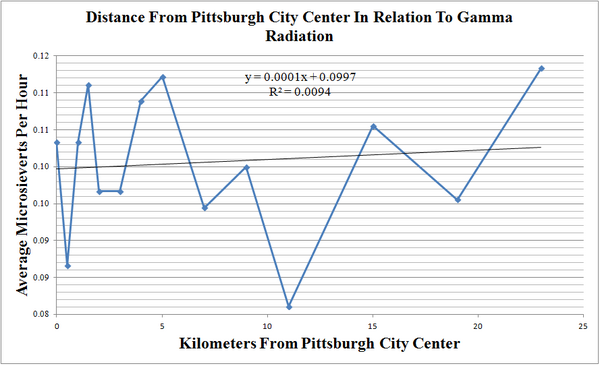
Gamma radiation can be produced by both natural and man-made sources and abnormally high exposure levels could lead to an increase in cell damage. In this study, gamma radiation was measured at different locations and any correlation with various geographic factors, such as distance from a city center, elevation and proximity to the nearest nuclear reactor, was determined.
Read More...