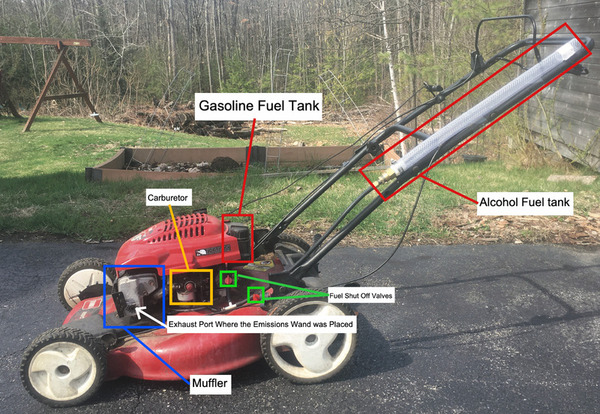
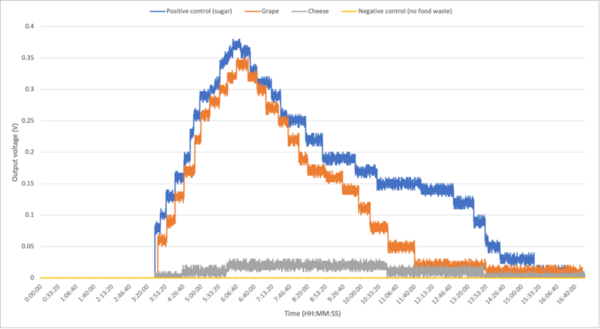
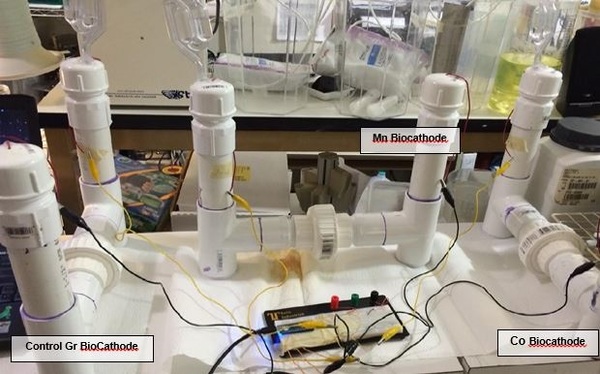
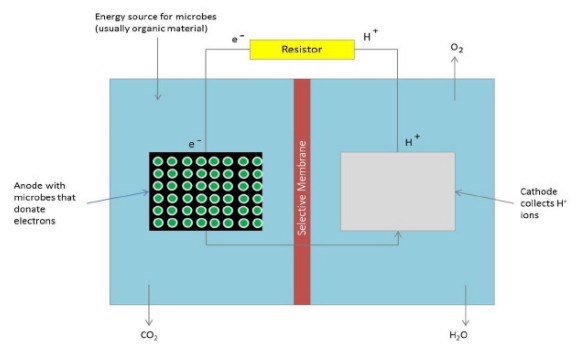
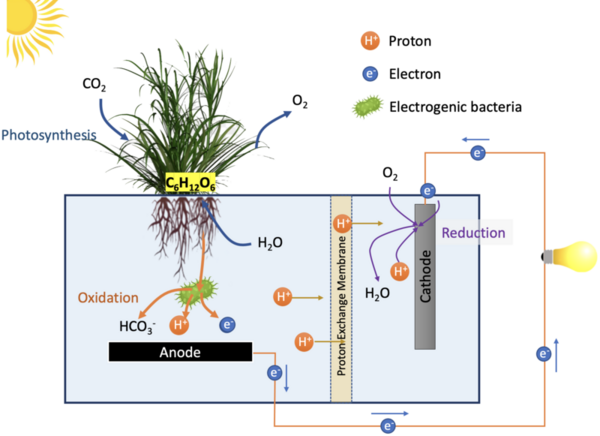
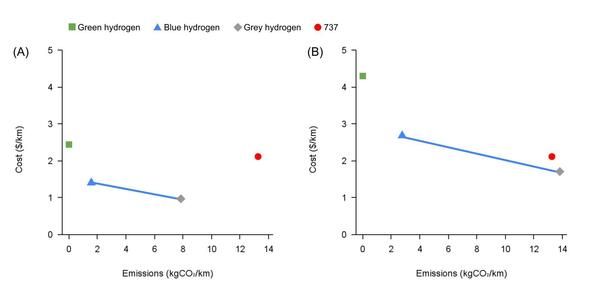
Here, the authors sought to investigate the efficiency, cost, and environmental impact of several possible propellants that are or could be used for space flight. By deriving three novel equations, they identified harm, energy, and cost scores for each fuel, suggesting that considering each factor will be essential to the ongoing growth of the space industry.
Read More....PNG)