.png)
In this study, the effects of different sources of serum on growing mesenchymal stem cells are compared with the goal of identifying one more suitable for clinical use.
Read More...A comparison study in the expansion of human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells
.png)
In this study, the effects of different sources of serum on growing mesenchymal stem cells are compared with the goal of identifying one more suitable for clinical use.
Read More...Examining the correlation between Massa Medicata Fermentata and Crohn’s disease: Implications for treatment and patient safety
Crohn’s disease is a chronic inflammatory bowel condition with symptoms like abdominal pain, fatigue, diarrhea, and malnutrition. Though there's no cure, various treatments help manage it. This study explored the potential impact of Massa Medicata Fermentata (MMF), a fermented Chinese herbal medicine containing Saccharomyces cerevisiae, on Crohn’s disease.
Read More...Mechanism and cytotoxicity of A1874 proteolysis targeting chimera on CT26 colon carcinoma cell line
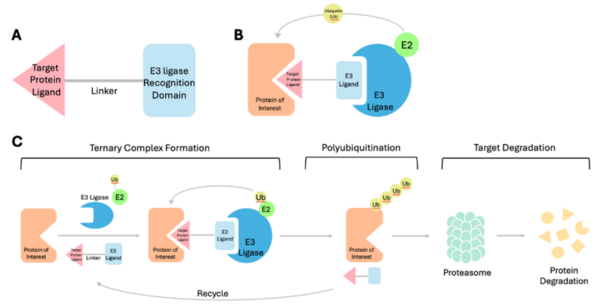
This study investigates the effects of the PROTAC compound A1874 on CT26 colon carcinoma cells, focusing on its ability to degrade the protein BRD4 and reduce cell viability. While A1874 had previously shown effectiveness in other colon cancer cell lines, its impact on CT26 cells was unknown.
Read More...Cocktail therapy to inhibit multispecies biofilm in cystic fibrosis patients
Here, recognizing the important role of bacterial biofilms in many life-threatening chronic infections, the authors investigated the effectiveness of a combination treatment on biofilms composed of up to three different common species within the lungs of cystic fibrosis patients with computational analysis. They found that a triple cocktail therapy targeting three different signaling pathways has significant potential as both a treatment and prophylaxis.
Read More...Effect of heme vs. non-heme iron supplements on gut microbiome fitness

Here, based on identification of iron deficiencies of a majority of people around the world, the authors sought to understand how the two main forms of dietary iron, heme and non-heme, affect the bacteria found in the human gut. by using a cell plate study, they found that bacterial growth increased with increasing concentration os either form of iron, up until the point where the high iron content resulted in cytotoxicity. They suggest this evidence points to the potential dangers of overconsumption of iron.
Read More...The Clinical Accuracy of Non-Invasive Glucose Monitoring for ex vivo Artificial Pancreas
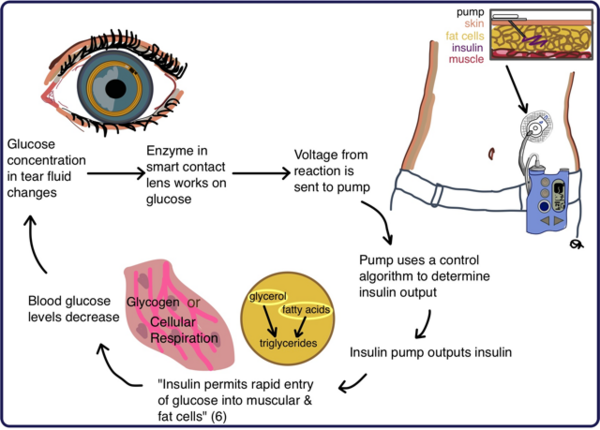
Diabetes is a serious worldwide epidemic that affects a growing portion of the population. While the most common method for testing blood glucose levels involves finger pricking, it is painful and inconvenient for patients. The authors test a non-invasive method to measure glucose levels from diabetic patients, and investigate whether the method is clinically accurate and universally applicable.
Read More...Evaluating the clinical applicability of neural networks for meningioma tumor segmentation on 3D MRI
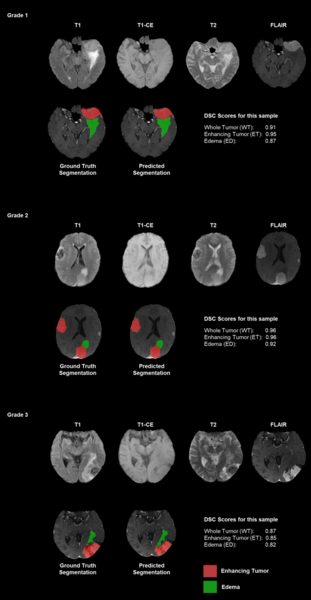
Authors emphasize the challenges of manual tumor segmentation and the potential of deep learning models to enhance accuracy by automatically analyzing MRI scans.
Read More...Lung cancer AI-based diagnosis through multi-modal integration of clinical and imaging data
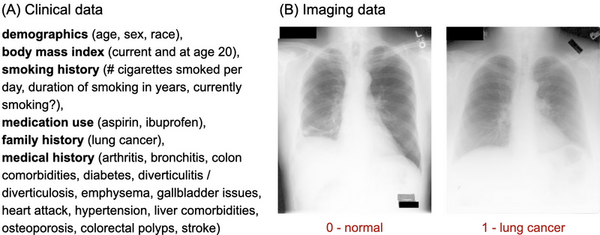
Lung cancer is highly fatal, largely due to late diagnoses, but early detection can greatly improve survival. This study developed three models to enhance early diagnosis: an MLP for clinical data, a CNN for imaging data, and a hybrid model combining both.
Read More...Reducing levels of C-Reactive Protein: An eight-week, open-label clinical trial of three oral supplements

In this study, the effects of vitamin C, ginger, or curcumin supplements on C-reactive protein levels in healthy participants are determined in an eight-week open-label trial.
Read More...Culturally Adapted Assessment Tool for Autism Spectrum Disorder and its Clinical Significance
Diagnosing of Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) using tools developed in the West is challenging in the Indian setting due to a huge diversity in sociocultural and economic backgrounds. Here, the authors developed a home-based, audiovisual game app (Autest) suitable for ASD risk assessment in Indian children under 10 years of age. Ratings suggested that the tool is effective and can reduce social inhibition and facilitate assessment. Further usage and development of Autest can improve risk assessment and early intervention measures for children with ASD in India.
Read More...