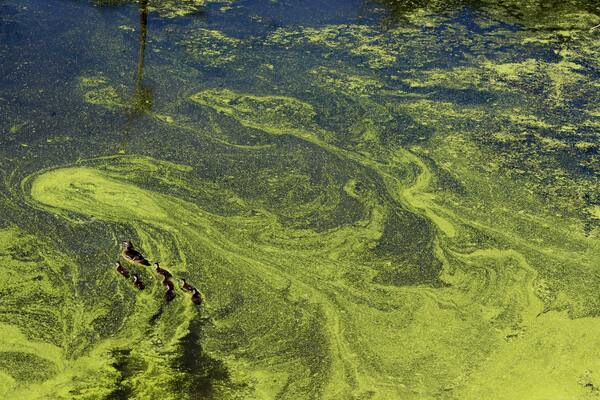
Algal overgrowth often threatens to clog irrigation pipes and drinking water lines when left unchecked, as well as releasing possible toxins that threaten plant and human health. It is thus important to find natural, non-harmful agents that can decrease algal growth without threatening the health of plants and humans. In this paper, the authors test the efficacy of barely extract in either liquid or pellet form in decreasing algal growth. While their results were inconclusive, the experimental set-up allows them to investigate a wider range of agents as anti-algal treatments that could potentially be adopted on a wider scale.
Read More...