
The authors looked at how storage temperature of potatoes can impact the sweetness of potatoes (due to the break down of the starch into simple sugars).
Read More...The impact of temperature on the hydrolysis of potato starches into simple sugars

The authors looked at how storage temperature of potatoes can impact the sweetness of potatoes (due to the break down of the starch into simple sugars).
Read More...Toxicity of aminomethylphosphonic acid via the Wnt signaling pathway as a novel mechanism

The Wnt signaling pathway, known to coordinate important aspects of cellular homeostasis ranging from differentiation, proliferation, migration, and much more, is dysregulated in many human diseases. This study demonstrates that aminomethylphosphonic acid, which is the main metabolite found in the common herbicide Glyphosate, is toxic to planaria and capable of binding to canonical Wnt proteins.
Read More...Application of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi to inhibit nitrogen uptake of weeds within crop fields
.jpg)
In this study, the ability of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi to limit the growth of an agricultural weed Cirsium arvense is tested. This has important implications for developing natural herbicides.
Read More...PCR technology for screening genetically modified soybeans

In order to determine whether unmarked soybeans in the market were genetically modified crops, the authors developed a polymerase chain reaction (PCR) screen for DNA lectin.
Read More...In vitro Comparison of Anticancer and Immunomodulatory Activities of Resveratrol and its Oligomers
Resveratrol is a type of stillbenoid, a phenolic compound produced in plants, that is known for its anti-inflammatory and anticancer effects. Many oligomers of resveratrol have recently been isolated their bioactivities remain unknown. Here, authors compared the bioactivities of resveratrol with natural dimers (ε-viniferin and gnetin H) and trimers (suffruticosol B and C). Results provide preliminary evidence that resveratrol oligomers could be potential preventive or therapeutic agents for cancers and other immune-related diseases
Read More...Lettuce seed germination in the presence of microplastic contamination

Microplastic pollution is a pressing environmental issue, particularly in the context of its potential impacts on ecosystems and human health. In this study, we explored the ability of plants, specifically those cultivated for human consumption, to absorb microplastics from their growing medium. We found no evidence of microplastic absorption in both intact and mechanically damaged roots. This outcome suggests that microplastics larger than 10 μm may not be readily absorbed by the root systems of leafy crops such as lettuce (L. sativa).
Read More...Detergent pollutants decrease nutrient availability in soil
Household detergents have surfactants that can potentially harm the soil and broader ecosystems. In this study, the authors investigate whether eco-friendly and less-eco-friendly detergents affect soil pH, phosphorus, nitrogen, and potassium levels.
Read More...Negative Effects of Pollution on English Daisy (Bellis perennis) Height and Flower Number
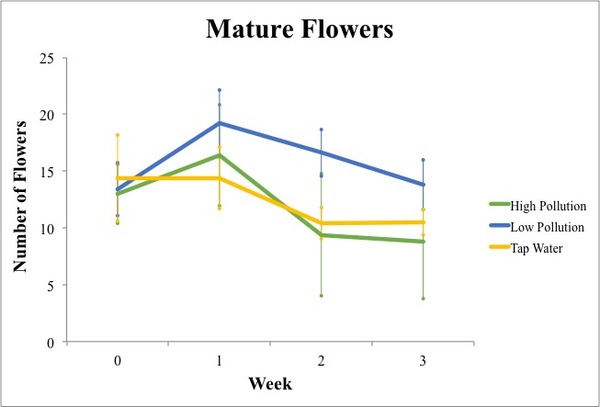
Chemicals used in fertilizers and pesticides often end up in nearby bodies of water due to runoff and may have negative impacts on these important ecosystems. In this study, the authors use water containing different nitrogen levels to investigate the effect on the growth of the English daisy.
Read More...Dispersing Agents Prevent Negative Impact of Oil on Uptake of Zinc by Duckweed (Lemna minor)
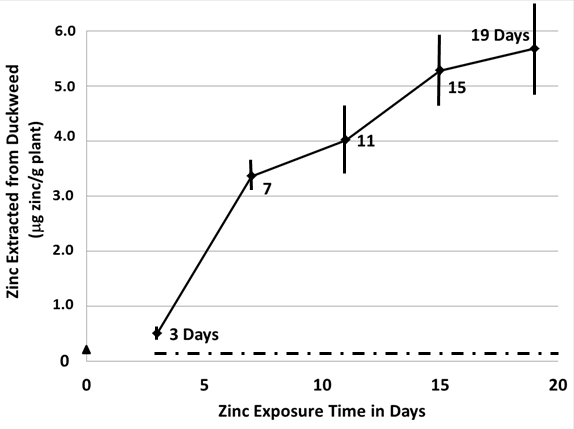
Duckweed plays an important role in its aquatic environment by removing pollutants, such as zinc, from the water. In this study, the authors demonstrate that uptake of zinc by duckweed is inhibited by the presence of oil in the water, but this effect can be reversed with the addition of a dispersing agent.
Read More...Investigating toxicity and antimicrobial properties of silver nanoparticles in Escherichia coli and Drosophila melanogaster
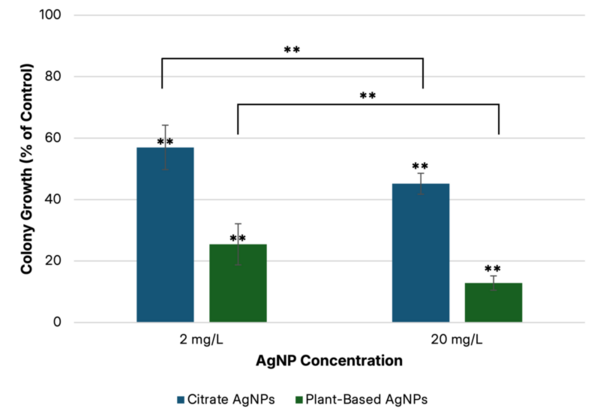
This paper looks at the antibacterial and toxic effects of silver nanoparticles (AgNPs) on Escherichia coli bacteria and Drosophila melanogaster fruit flies. They modified the AgNPs size, concentration, and surface coating to determine the effects on each of the organisms. For both organisms, increased AgNP concentration demonstrated increased toxicity but particle size and surface coating had opposing effects.
Read More...