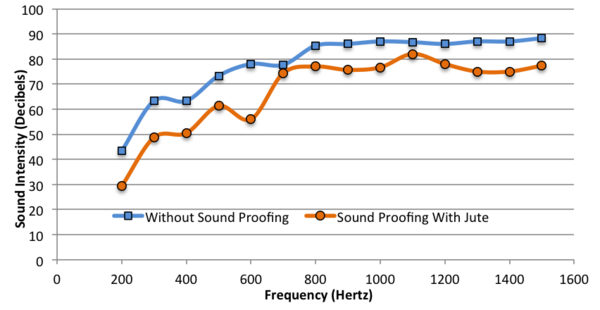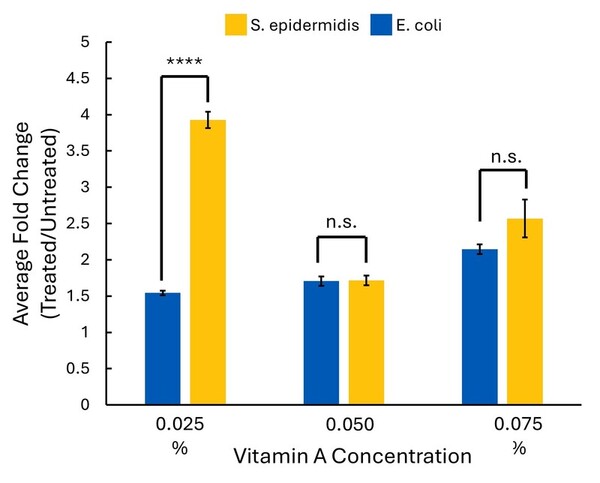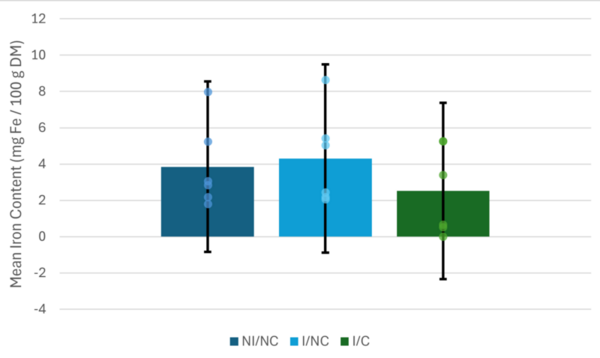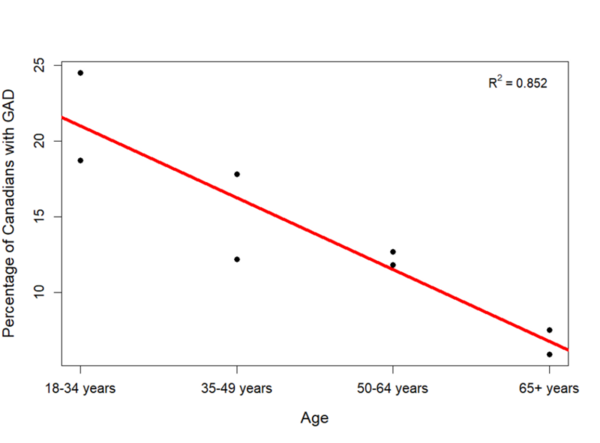
The impact of age on mental health is a crucial yet understudied aspect of public health. While mental health is gaining recognition as a vital component of overall well-being, its correlation with age remains largely unexplored. In Canada, where the median age has risen significantly over the past half-century, understanding this relationship becomes increasingly pertinent. Researchers hypothesized that older adults would exhibit lower rates of mental health disorders and report better perceived mental health due to increased emotional stability and maturity.
Read More...